Abstract
This research aimed to develop, validate, and test a questionnaire that university undergraduate students can use to gauge their self-regulation skills (SRS). The researchers developed the questionnaire's items through a review of related literature and then validated them with a panel of specialists, i.e., PhDs. The questionnaire's validity was checked using EFA and quantitative methods. One hundred university students aged seventeen to twenty became part of the study's sample. At first, a 66-item questionnaire was developed using a thematic analysis of the qualitative part. An expert panel verified that the questionnaire was valid regarding its substance. After eliminating duplicates and irrelevant questions, a final questionnaire consisting of 27 items was developed. The four basic constructs of self-regulation skills are behavioral regulation, cognitive regulation, emotional regulation, and self-compassion. Researchers employed the tool to gauge university students' ability to self-regulate through four self-regulatory skills constructs.
Key Words
Development and Validation, Instrument, Self-Regulation Skills, University Level
Introduction
Since students are increasingly expected to be independent learners and managers of their academic responsibilities in higher education, self-regulation has gained prominence in educational psychology (Zimmerman, 2000). People with strong self-regulation skills can control their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors in a way that helps them reach their goals (Schunk & Zimmerman, 1998). Students' capacity to develop, implement, and assess their learning strategies is directly correlated to their achievement in the classroom (Pintrich, 2004). Nota et al. (2004) argue that standardized measures should be developed to evaluate self-regulation abilities at the university level, even though self-regulation is acknowledged as important in education.
Students' ability to self-regulate has been a focal point of recent curriculum changes. On the other hand, these changes have yet to recently improve student outcomes (Graham et al., 2005). This disparity may be because schools need to prioritize developing students' capacity for self-regulation in the classroom (Hutchinson et al., 2021). According to Wolters (2003), students may find it more challenging to acquire self-regulatory behaviors in traditional curricula due to their emphasis on strict learning and evaluation processes.
According to Zimmerman (2002), there are multiple facets to the educational self-regulation framework, including cognitive, metacognitive, motivational, and behavioral components. Strategies for processing information, like elaboration and summary, are part of cognitive self-regulation (Pintrich, 2000). Metacognitive self-regulation is the capacity to monitor and manage one's thought processes (Schraw & Dennison, 1994). Setting goals, believing in one's abilities, and being intrinsically motivated are all aspects of motivational self-regulation (Bandura, 1997); time management and environmental structuring are examples of behavioral self-regulation.
Because of the increased independence and responsibility that students experience in higher education, self-regulation becomes even more important (Nota et al., 2004). Students with strong self-regulation skills can better manage the demands of university life, maintain academic progress, and adjust to their new surroundings (Richardson et al., 2012). Regardless, self-regulation is challenging for many college students, resulting in slacking off in class, failing to meet expectations, and even dropping out (Steel, 2007).
Numerous studies have investigated self-regulation; however, additional research is required to design and validate standardized instruments uniquely suited to university students (Cleary, 2011). Additional psychometric features are typically required for existing measures to be reliable and valid across varied university populations (Boekaerts & Corno, 2005). Winne and Perry (2000) state a pressing need for a reliable tool to evaluate college students' ability to self-regulate since this will provide light on areas that could benefit from support services and educational interventions.
According to social cognitive theory, which the SRS instrument is based on, self-regulation is affected by a complex web of factors that include individual, behavioral, and contextual aspects (Bandura, 1986). Learners who can self-regulate do things like make plans, track their progress, and change their approach until they reach their objectives (Zimmerman, 2000). Schunk (2001) posits that the self-regulation instrument, which evaluates students' self-regulatory behaviors in various settings and tasks, intends to capture this evolving process.
Creating an accurate and trustworthy SRS instrument has far-reaching consequences for educational practice. Educators can utilize it to pinpoint pupils who could benefit from tailored interventions to help them build self-regulation abilities. This instrument can also inform curriculum and pedagogical approaches that promote student self-regulation of learning (Boekaerts, and Corno, 2005). Higher education academic success variables can be better understood with the help of the SRS instrument, which offers a thorough evaluation of self-regulation (Wolters, 2003). Ultimately, enhancing educational results necessitates creating and validating a university-level instrument measuring self-regulation skills. The Self-Regulation Skills Instrument, a generally valid and trustworthy self-regulation measure, can be used to understand how university students can enhance their studying and homework activities.
Review of Related Literature
University students need self-regulation to control emotions, behaviors, and thoughts to achieve goals and stay healthy. University educators, psychologists, and researchers must develop and validate a self-regulation skills (SRS) assessment. This literature review examines four self-regulation dimensions: behavioral, cognitive, emotional, and self-compassion.
Behavioral self-regulation is controlling activities and behaviors to achieve personal goals. Academically, pupils must defer gratification and persevere, making self-regulation essential. Zimmerman (2000) says self-regulated learners set goals, manage time, and self-monitor to succeed academically. According to Bandura's (1986) social cognitive theory, people can manage their behavior through self-observation, self-judgment, and self-reaction. Pintrich (2000) found that students with excellent behavioral self-regulation do better academically. Wolters (2003) observed that students who planned and self-monitored had higher marks and academic satisfaction.
Behavioral self-regulation instruments typically measure the frequency and effectiveness of various techniques. The Self-Regulated Learning Interview Schedule (SRLIS) and Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ) are popular instruments in this field (Pintrich, 1991). However, university students require a comprehensive self-regulation tool that includes behavioral factors. Controlling attention, memory, and problem-solving is cognitive self-regulation. Students need this dimension to plan, monitor, and assess their learning (Winne & Perry, 2000). Cognitive self-regulation helps students adjust to changing pressures and persevere.
Metacognition—the knowledge and control of one's cognitive processes—is crucial to cognitive self-regulation theories (Flavell, 1979). Auto-questioning and summarizing improve learning and understanding (Schraw and Dennison, 1994). Azevedo and Cromley (2004) found that metacognitive students did better in hypermedia learning. Cognitive self-regulation is assessed by examining students' metacognitive methods and cognitive resource regulation. Metacognitive Awareness Inventory (MAI) and Learning and Study Strategies Inventory (LASSI) are popular measurements. However, higher education cognitive self-regulation is dynamic and context-specific; therefore, instruments are needed.
Healthy and adaptive emotional self-regulation involves managing and responding to emotions. University students who experience stress and emotional issues need this talent. Gross (1998) defines emotional self-regulation as recognizing, modulating, and coping with emotions. Research shows that emotionally regulated children can bear academic pressure and perform well (Pekrun, 2021). Schutz and Davis (2000) discovered that adaptive emotion management strategies, including cognitive reappraisal and problem-solving, reduced anxiety and improved academic performance.
The Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (ERQ) and Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale (DERS) measure emotional self-regulation (Gratz & Roemer, 2004). These instruments measure emotional awareness and management strategies. However, the need for comprehensive tools that combine emotional self-regulation with other self-regulation characteristics is developing.
Self-compassion, a novel concept in self-regulation, entails being gentle to oneself when things go wrong. According to Neff (2003), self-compassion includes self-kindness, common humanity, and awareness. Self-compassion boosts resilience and well-being, which are essential for academic performance. Self-compassion has been linked to lower stress, more motivation, and better academic performance (Neff et al., 2005). It is observed that self-compassionate students used adaptive coping mechanisms and had lower burnout rates. The Self-Compassion Scale (SCS) is commonly used to measure self-compassion (Neff, 2003). It evaluates self-compassionate behavior and attitudes. By including self-compassion in the assessment, students' self-regulation abilities can be more fully understood.
The literature review emphasizes the complexity of self-regulation and the need for a comprehensive university-level self-regulation tool. Students' academic achievement and well-being depend on behavioral, cognitive, emotional, and self-compassion self-regulation. Existing tools provide valuable insights but frequently focus on specific self-regulation features. An integrated strategy that captures the complexity and interrelatedness of these characteristics is needed to better understand higher education self-regulation.
Research Methodology
Different researchers developed tools to assess self-regulation i.e. Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ) and the Self-regulation Questionnaire (SRQ) (Pintrich, 2000). Nota et al. (2004) noted that the tools above were mostly designed for younger students or the general public. Thus, they might need to thoroughly address the specific difficulties that college students encounter when trying to self-regulate. Moreover, current assessments must consider the cultural contextual elements that impact self-regulation in various educational contexts (Purdie et al., 1996). Considering these limitations, the present study will design and test an innovative self-regulation skill evaluation tool for college students. Schunk and Zimmerman (1998) state that a comprehensive literature review on self-regulation is the first step in the development process. Then, a basic set of items representing the many aspects of self-regulation is created. After expert assessment and pilot testing, we will fine-tune the items to ensure the content is valid and easy to grasp (DeVellis, 2016).
Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses will be conducted as part of the validation process to determine the instrument's concept validity and investigate its factorial structure (Brown, 2015). Reliability analyses will evaluate the instrument's internal consistency (Cortina, 1993). Examining the relationships between the SRS scores and associated factors, such as academic performance and motivation, would also help evaluate criterion-related validity (Messick, 1995).
Participants
The research was conducted with the participation of one hundred undergraduate students to understand self-regulation skills (SRS). A convenient sampling approach was utilized to select pupils from two faculties i.e. Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences; Faculty of Management Sciences. The sample consisted of thirty-four males and sixty-six females (See Table 1), all of whom were enrolled in undergraduate programs and were between the ages of seventeen and twenty. Urdu and Punjabi were found to be the most common native languages among the participants, with English serving as a supplementary language of instruction.
Table 1
|
Category |
Frequency
/ Percentage |
|
Male |
34
(34%) |
|
Female |
66 (66%) |
Research Design
An exploratory sequential mixed methods approach was utilized to investigate self-regulation's capabilities. The first step in this design is to collect and analyze qualitative data, and then the next step is to collect and analyze quantitative data. One of its advantages is that it is straightforward and allows in-depth research on the quantitative results. The researchers described four phases for the execution of the study. In the initial two phases, the researchers developed the (SRS) questionnaire through the literature and part of the qualitative perspective of the study. Whereas the questionnaire validation is the focus of the latter two phases. The current study employed an exploratory sequential mixed methods approach to explore self-regulation skills among university students. Initially, this study explored self-regulation skills qualitatively through literature and expert opinions of the professionals in the field and ultimately this allowed for in-depth research on quantitative results.
Phase-I
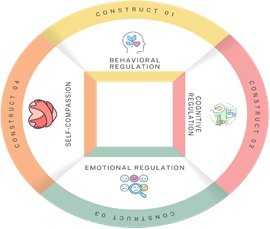
At this very phase, the researcher explored various themes to theorize the constructs for self-regulation skills. The qualitative side of the study informed about the essential dimensions of self-regulation skills i.e. cognitive regulation (CR), behavioral regulation (BR), emotional regulation (ER), and self-compassion (SC) (Figure 1). It was affirmed after the minute evaluation of the qualitative aspects. Students' ability to gain control over their actions, feelings, emotions and thoughts are central to these involved with the mentioned components of self-regulation skills. Self-regulation skills not only have a significant contribution toward persistent learning outcomes but also have impacts on long-term academic success and personal development.
Figure 1
Phase-II
The second phase of the study involved developing the items for the questionnaire and furthermore to refining them by competent professionals in the field. In this way, researchers achieved successful face and content validity of the said questionnaire. Prior to all this, an inclusive review of the literature and in-depth discussion/interviews with the professionals were used for the development of the self-regulation skills questionnaire. An initial questionnaire was developed with 66 items to cover the broad spectrum of abilities related to self-regulation skills. Furthermore, researchers again contacted to authenticate the questionnaire had precise information with a group of three educators i.e. each of them having PhD degree in Education or English and had ten years of professional experience in the field. The mentioned experts evaluated the items based on how easily the students could understand, the relevance of the items, precision, and comprehensiveness. It is already mentioned that there were 66 items but after getting feedback from the experts these items were reduced to 35. Moreover, during the procedure to refine the questionnaire, it is ensured that it accurately apprehends the attributes of behavior, cognition, emotions, and self-compassion patterns. The language of the questionnaire was English because the students who sampled the study had English as the language of instruction.
Phase 3
Among the one hundred university students who participated in the survey, there were 66 female and 34 male university students between the ages of 17 and 20. The questionnaire that had been developed was distributed to the students. The researchers took consent from the institution's administration so that the study followed ethical norms for the collection of data from the respondents. Participants' privacy was preserved throughout the process of data collection as well as the execution of the study. Questionnaire items related to the four constructs i.e. cognitive regulation, behavioral regulation, emotional regulation, and self-compassion that were cohesively merged into the final questionnaire having 27 items. The research distributed the final version of the questionnaire having a Likert scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) while the respondents were asked to rate the degree to which they agreed or disagreed with each item in the questionnaire. By completing the questionnaire, the students could acquire substantial insights into their capacity to regulate their cognitive, behavioral, and emotional states. This contributed to a more comprehensive knowledge of the self-regulatory skills that university students share.
Phase 4
In order to study the structure of the questionnaire, the researchers applied an exploratory factor analysis (EFA) method at this phase of the research process. The most important goal was to ascertain the degree to which the questions on the questionnaire were compatible with one another and, if necessary, to cut down on the overall number of items included in the questionnaire. Cronbach's alpha statistic was another statistic that we computed in order to ascertain whether or not all of the items contained in the questionnaire were consistent with one another. The researchers obtained fundamental statistics for each of the items in order to study the relationships between them. These statistics included the average scores each item earned and the degree to which each item deviated from the others. The computations in question were carried out with the assistance of a piece of software known as SPSS 27.0.
Table 2
|
KMO Measure of Sampling
Adequacy. |
.843 |
|
|
Bartlett's Test of
Sphericity |
Approx. Chi-Square |
3289.725 |
|
df |
351 |
|
|
Sig. |
.000 |
|
Table 3
|
Item No. |
MS |
SD |
Alpha |
MS |
SD |
|
I11 |
3.94 |
0.862 |
0.720 |
3.935 |
.661 |
|
I9 |
3.91 |
0.854 |
|||
|
I10 |
3.90 |
0.927 |
|||
|
I4 |
3.99 |
1.059 |
|||
|
I5 |
4.17 |
0.739 |
0.687 |
4.004 |
0.472 |
|
I7 |
3.65 |
0.857 |
|||
|
I3 |
4.00 |
0.841 |
|||
|
I6 |
3.96 |
0.840 |
|||
|
I2 |
4.16 |
0.762 |
|||
|
I1 |
3.89 |
0.764 |
|||
|
I8 |
4.20 |
0.804 |
|||
|
I20 |
3.93 |
0.9.2 |
0.963 |
3.809 |
0.824 |
|
I18 |
3.83 |
0.954 |
|||
|
I22 |
3.82 |
0.947 |
|||
|
I17 |
3.92 |
0.971 |
|||
|
I16 |
3.90 |
0.937 |
|||
|
I19 |
3.73 |
1.024 |
|||
|
I21 |
3.76 |
1.016 |
|||
|
I23 |
3.74 |
0.939 |
|||
|
I12 |
3.80 |
1.015 |
|||
|
I13 |
3.75 |
1.038 |
|||
|
I15 |
3.84 |
1.032 |
|||
|
I14 |
3.69 |
0.982 |
|||
|
I25 |
3.86 |
0.899 |
0.913 |
3.880 |
0.862 |
|
I24 |
3.96 |
0.942 |
|||
|
I26 |
4.01 |
0.969 |
|||
|
I27 |
3.69 |
1.089 |
Table 4
|
Items |
Initial |
Extraction |
|
I1 |
1.000 |
.700 |
|
I2 |
1.000 |
.677 |
|
I3 |
1.000 |
.658 |
|
I4 |
1.000 |
.750 |
|
I5 |
1.000 |
.781 |
|
I6 |
1.000 |
.562 |
|
I7 |
1.000 |
.644 |
|
I8 |
1.000 |
.641 |
|
I9 |
1.000 |
.866 |
|
I10 |
1.000 |
.841 |
|
I11 |
1.000 |
.868 |
|
I12 |
1.000 |
.739 |
|
I13 |
1.000 |
.660 |
|
I14 |
1.000 |
.619 |
|
I15 |
1.000 |
.698 |
|
I16 |
1.000 |
.747 |
|
I17 |
1.000 |
.772 |
|
I18 |
1.000 |
.823 |
|
I19 |
1.000 |
.720 |
|
I20 |
1.000 |
.868 |
|
I21 |
1.000 |
.689 |
|
I22 |
1.000 |
.788 |
|
I23 |
1.000 |
.694 |
|
I24 |
1.000 |
.823 |
|
I25 |
1.000 |
.923 |
|
I26 |
1.000 |
.843 |
|
I27 |
1.000 |
.632 |
Table 5
|
Component |
Initial Eigenvalues |
Extraction Sums of
Squared Loadings |
Rotation Sums of
Squared Loadings |
||||
|
Total |
% of Variance |
Cumulative % |
Total |
% of Variance |
Cumulative % |
Total |
|
|
1 |
14.053 |
52.048 |
52.048 |
14.053 |
52.048 |
52.048 |
14.038 |
|
2 |
3.512 |
13.007 |
65.055 |
3.512 |
13.007 |
65.055 |
3.402 |
|
3 |
1.274 |
4.719 |
69.774 |
1.274 |
4.719 |
69.774 |
1.388 |
|
4 |
1.190 |
4.406 |
74.180 |
1.190 |
4.406 |
74.180 |
1.201 |
|
5 |
.951 |
3.523 |
77.703 |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
.834 |
3.087 |
80.791 |
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
.702 |
2.599 |
83.389 |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
.592 |
2.191 |
85.581 |
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
.514 |
1.904 |
87.485 |
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
.473 |
1.752 |
89.237 |
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
.446 |
1.653 |
90.890 |
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
.401 |
1.486 |
92.376 |
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
.391 |
1.449 |
93.825 |
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
.335 |
1.240 |
95.065 |
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
.264 |
.978 |
96.044 |
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
.219 |
.811 |
96.855 |
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
.198 |
.734 |
97.589 |
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
.145 |
.538 |
98.127 |
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
.129 |
.479 |
98.606 |
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
.089 |
.328 |
98.934 |
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
.080 |
.297 |
99.232 |
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
.064 |
.237 |
99.468 |
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
.055 |
.205 |
99.673 |
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
.037 |
.137 |
99.810 |
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
.027 |
.101 |
99.911 |
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
.017 |
.062 |
99.972 |
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
.007 |
.028 |
100.000 |
|
|
|
|
Table 6
|
Items |
Component |
|||
|
BR,
ER, SC |
BR, CR |
CR |
CR |
|
|
I remind myself that most students feel
unsure sometimes. |
.940 |
|
|
|
|
I feel most other students are doing better
than I am. |
.924 |
|
|
|
|
I copy my notes over to help me remember the
material. |
.921 |
|
|
|
|
I keep working with uninteresting materials
until I finish them. |
.918 |
|
|
|
|
I practice saying the important facts over
and over to myself. |
.903 |
|
|
|
|
I try to be supportive of myself as a
student. |
.896 |
|
|
|
|
I tend to be tough on myself as a student. |
.893 |
|
|
|
|
I get over-excited with my feelings. |
.880 |
|
|
|
|
I see my failings as part of the human
condition. |
.875 |
|
|
|
|
I feel cut off from other students. |
.854 |
|
|
|
|
I’m disapproving and judgmental about myself
as a student. |
.848 |
|
|
|
|
I’m intolerant and impatient towards myself. |
.846 |
|
|
|
|
I feel alone in my failure. |
.829 |
|
|
|
|
Little things can seem like a big deal to
me. |
.819 |
|
|
|
|
I pay attention to my feelings. |
.811 |
|
|
|
|
I allow my feelings to affect my thoughts. |
.805 |
|
|
|
|
When I take Tests I have upset feeling. |
.798 |
|
|
|
|
I try to think about pleasant things when I
am sad. |
.741 |
|
|
|
|
I try to approach the experience with
curiosity and openness. |
.740 |
|
|
|
|
I choose topics that teach me, even if they
require more work. |
|
.831 |
|
|
|
I try to predict problems that might happen
with my learning. |
|
.823 |
|
|
|
I evaluate my learning processes with the
aim of improving them. |
|
.764 |
|
|
|
I control and evaluate the solution. |
|
.760 |
|
|
|
I assess how much I am learning during a
learning task. |
|
.665 |
|
|
|
I interpret the outcome and formulate an
answer. |
|
.563 |
|
|
|
I create a picture of the problem. |
|
|
.828 |
|
|
I ask myself questions to ensure I
understand the material. |
|
|
|
.800 |
Conclusion
The study proved an effective and reliable self-regulation tool with 27 items that assess self-regulation skills among university students in Pakistan. In this study, the self-regulation skills related to the four basic constructs i.e. cognitive regulation, behavioral regulation, emotional regulation, and self-compassion. The mentioned constructs contribute a conceptual framework for a comprehensive understanding of the self-regulation skills of university students. Cognitive regulation refers to the mental process that is responsible and makes the work easier in monitoring, organizing, and evaluating professional and academic responsibilities. Whereas behavioral regulation refers to the behaviors and actions toward learning activities within the premises of the university and outside the institutions. In a university, the term emotional regulation refers to approaches that students use to control and manage their emotions and feelings efficiently. Last but not least self-compassion refers to the behavior that university students retain in times of difficulty and displeasure. The mentioned tool has the capacity to efficiently evaluate university students' capacity for self-regulation skills rather it also provides instructions on university students' self-regulation abilities.
In summary, this 27-item fabricated tool is an effective testing instrument for university students' self-regulation skills in different four dimensions at the university level. The researchers are motivated and hopeful toward the effective usability of the tool which is a collaborative work and furthermore, it could contribute to and value understanding for university students in their studies and learning processes. Surely, the researchers will share some of the promising insights with academicians, professionals, and researchers in the future related to the self-regulation skills (SRS) of university students.
References
-
Azevedo, R., & Cromley, J. G. (2004). Does training on Self-Regulated Learning facilitate students’ learning with Hypermedia? Journal of Educational Psychology, 96(3), 523–535. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.96.3.523
Google Scholar Fulltext - Bandura, A. (1986). Social Foundations of Thought and Action : A Social Cognitive Theory. Prentice-Hall. https://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10010087207/ Google Scholar Fulltext
- Boekaerts, M., & Corno, L. (2005). Self-Regulation in the Classroom: A Perspective on Assessment and Intervention. Applied Psychology, 54(2), 199–231. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-0597.2005.00205.x
- Brown, A. L. (2015). Confirmatory factor analysis for applied research. Guilford Publications. Google Scholar Fulltext
- Cleary, T. J. (2011). Emergence of Self-Regulated Learning Microanalysis : Historical Overview, Essential Features, and Implications for Research and Practice University of Wisconsin – Milwaukee. In Handbook of Self-regulation of Learning and Performance, 343–359. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203839010-28 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Cortina, J. M. (1993). What is coefficient alpha? An examination of theory and applications. Journal of Applied Psychology, 78(1), 98–104. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.78.1.98 Google Scholar Fulltext
- DeVellis, R. F. (2016). Scale development: Theory and applications (4th ed.). Sage. Google Scholar Fulltext
- Flavell, J. H. (1979). Metacognition and cognitive monitoring: A new area of cognitive–developmental inquiry. American Psychologist/˜the œAmerican Psychologist, 34(10), 906–911. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066x.34.10.906 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Graham, S., Harris, K. R., & Mason, L. (2005). Improving the writing performance, knowledge, and self-efficacy of struggling young writers: The effects of self-regulated strategy development. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 30(2), 207–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2004.08.001 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Gross, J. J. (1998). The Emerging Field of Emotion Regulation: An Integrative Review. Review of General Psychology, 2(3), 271–299. https://doi.org/10.1037/1089-2680.2.3.271 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Hutchinson, L. R., Perry, N. E., & Shapka, J. D. (2021). Assessing young children’s self-regulation in school contexts. Assessment in Education, 28(5–6), 545–583. https://doi.org/10.1080/0969594x.2021.1951161 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Messick, S. (1995). Validity of psychological assessment: Validation of inferences from persons’ responses and performances as scientific inquiry into score meaning. American Psychologist/˜the œAmerican Psychologist, 50(9), 741–749. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066x.50.9.741 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Neff, K. D. (2003). The development and validation of a scale to measure Self-Compassion. Self and Identity, 2(3), 223–250. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298860309027
- Neff, K. D., Hsieh, Y., & Dejitterat, K. (2005). Self-compassion, Achievement Goals, and Coping with Academic Failure. Self and Identity, 4(3), 263–287. https://doi.org/10.1080/13576500444000317 Google Scholar Google Scholar Fulltext Fulltext
- Nota, L., Soresi, S., & Zimmerman, B. J. (2004). Self-regulation and academic achievement and resilience: A longitudinal study. International Journal of Educational Research, 41(3), 198–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2005.07.001 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Pekrun, R. (2021). Teachers need more than knowledge: Why motivation, emotion, and self-regulation are indispensable. Educational Psychologist :/Educational Psychologist, 56(4), 312–322. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2021.1991356 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Pintrich, P. R. (1991). A Manual for the Use of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ). . http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED338122.pdf Google Scholar Fulltext
- Pintrich, P. R. (2000). The role of Goal orientation in Self-Regulated Learning. In Elsevier eBooks (pp. 451–502). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-012109890-2/50043-3 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Pintrich, P. R. (2004). A Conceptual Framework for Assessing Motivation and Self-Regulated Learning in College Students. Educational Psychology Review, 16(4), 385–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-004-0006-x Google Scholar Fulltext
- Purdie, N., Hattie, J., & Douglas, G. (1996). Student conceptions of learning and their use of self-regulated learning strategies: A cross-cultural comparison. Journal of Educational Psychology, 88(1), 87–100. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.88.1.87 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Richardson, M., Abraham, C., & Bond, R. (2012). Psychological correlates of university students’ academic performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 138(2), 353–387. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026838
- Schraw, G., & Dennison, R. S. (1994). Assessing metacognitive awareness. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 19(4), 460–475. https://doi.org/10.1006/ceps.1994.1033
- Schunk, D. H. (2001). Self-regulation through goal setting. ERIC Digest.
- Schunk, D. H., & Zimmerman, B. J. (1998). Self-regulated learning : from teaching to self-reflective practice. In Guilford Publications eBooks. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BA36326681
- Schutz, P. A., & Davis, H. A. (2000). Emotions and Self-Regulation during Test taking. Educational Psychologist :/Educational Psychologist, 35(4), 243–256. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326985ep3504_03
- Steel, P. (2007). The nature of procrastination: A meta-analytic and theoretical review of quintessential self-regulatory failure. Psychological Bulletin, 133(1), 65–94. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.133.1.65 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Winne, P. H., & Perry, N. E. (2000). Measuring Self-Regulated Learning. In Elsevier eBooks (pp. 531–566). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-012109890-2/50045-7
- Wolters, C. A. (2003). Regulation of Motivation: Evaluating an underemphasized aspect of Self-Regulated Learning. Educational Psychologist :/Educational Psychologist, 38(4), 189–205. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326985ep3804_1
- Zimmerman, B. J. (2000). Attaining Self-Regulation. In Elsevier eBooks (pp. 13–39). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-012109890-2/50031-7
- Zimmerman, B. J. (2002). Becoming a Self-Regulated Learner: An Overview. Theory Into Practice, Digital/Theory Into Practice, 41(2), 64–70. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15430421tip4102_2
Cite this article
-
APA : Ali, M. Q., Jabeen, Q., & Rafeeq, K. (2024). Development and Validation of an Instrument on Self-Regulation Skills (SRS) at the University Level. Global Educational Studies Review, IX(II), 75-87. https://doi.org/10.31703/gesr.2024(IX-II).10
-
CHICAGO : Ali, Muhammad Qasim, Qudsia Jabeen, and Khadija Rafeeq. 2024. "Development and Validation of an Instrument on Self-Regulation Skills (SRS) at the University Level." Global Educational Studies Review, IX (II): 75-87 doi: 10.31703/gesr.2024(IX-II).10
-
HARVARD : ALI, M. Q., JABEEN, Q. & RAFEEQ, K. 2024. Development and Validation of an Instrument on Self-Regulation Skills (SRS) at the University Level. Global Educational Studies Review, IX, 75-87.
-
MHRA : Ali, Muhammad Qasim, Qudsia Jabeen, and Khadija Rafeeq. 2024. "Development and Validation of an Instrument on Self-Regulation Skills (SRS) at the University Level." Global Educational Studies Review, IX: 75-87
-
MLA : Ali, Muhammad Qasim, Qudsia Jabeen, and Khadija Rafeeq. "Development and Validation of an Instrument on Self-Regulation Skills (SRS) at the University Level." Global Educational Studies Review, IX.II (2024): 75-87 Print.
-
OXFORD : Ali, Muhammad Qasim, Jabeen, Qudsia, and Rafeeq, Khadija (2024), "Development and Validation of an Instrument on Self-Regulation Skills (SRS) at the University Level", Global Educational Studies Review, IX (II), 75-87
-
TURABIAN : Ali, Muhammad Qasim, Qudsia Jabeen, and Khadija Rafeeq. "Development and Validation of an Instrument on Self-Regulation Skills (SRS) at the University Level." Global Educational Studies Review IX, no. II (2024): 75-87. https://doi.org/10.31703/gesr.2024(IX-II).10
