Abstract
This case study specifically examines flaws in the design of online conversations created using Salmon's five-stage model, and highlights how easy it is to overlook key aspects when planning an online campaign. In the case study, the topics chosen for discussion failed to resonate with many students on a personal level. This demonstrates the importance of identifying flaws in the design of online conversations created using Salmon's five-stage model and highlights how easily these issues can be overlooked during event planning. It emphasizes the concept that participation is a prerequisite for community development. This article, therefore, explores how skilled community development practitioners can effectively address and overcome barriers to participation by stimulating personal and emotional interest. By understanding the importance of relationships and emotional engagement, educators can create online activities that truly motivate and engage students, resulting in a more vibrant and engaging online learning community.
Key Words
Student Engagement, Online Discussion, Salmon's five-stage Model, Education
Introduction
Learning regularly takes location in communal putting wherein involvement in collective sports creates a network of exercise (Handbook of Research on Online Discussion-Based Teaching Methods - Google Books, n.d.). Online dialogue has advanced as an interest wherein humans engage to assemble knowledge, negotiate that means and thereby create a network of inexperienced persons (Andrew, n.d.). Lively input in both face-to-face and online dialogue is a preference for college students, and now and again college students select now no longer to sign up Potentially college students who determine now no longer to contribute lose possibilities for learning (Thornicroft et al., 2010).
In Browning's case have a look at the education-created supportive surroundings fostering trust, however, his principal factor is that achievement relied on a formative evaluation interest designed to inspire social interaction (Hossain et al., 2023). Each scholar added every other scholar to the institution in the on-line space, growing an experience of belonging and a snug medium for making friends(Handbook of Research on Online Discussion-Based Teaching Methods - Google Books, n.d.) (Thornicroft et al., 2016).
The enjoy reviewed underneath indicates how smooth it is miles to make errors in designing dialogue; it examines a particular instance wherein college students shed mild bad motivation for participation (Elshami et al., 2022). This instance concerned 35 new undergraduates analyzing control in 2 disciplines such as network development (Hou et al., 2023). Community engagement theory, derived from exercise in assist instructors enhance scholar engagement in on-line communities as shown in figure 1: A study farm work of quality learning achievement. This article applies those thoughts to decorate the reports of inexperienced persons through on-line dialogue bolstered through private means (Proceedings of the Future Technologies Conference (FTC) 2019: Volume 2 - Google Books, n.d.) (Khokhar, Hou, et al., 2020).
Figure 1

Literature Review
Empowered with the guide of utilizing a commitment to the cost of on-line discourse as a sort of imperative component for fostering an organization of students, educators may likewise mostly detect distress while understudies neglect to generally be a piece of, or so they kind of thought. "I for all intents and purposes had persistently specifically guessed that as fast on the grounds that the definitely computerized school room entryway basically opened up at the start of the semester, my understudies may definitely come pouring through, but this essentially has now as of now not consistently been the situation for all undergrads" (HOU et al., 2021) (Drinking spree 23003, 347), contrary to popular belief.
The Value of Participation and Community Development Theory
Cooperation in concentrating on the network depends upon first on an understudy being sort of gifted and besides at the student associating with others with the guide of utilizing making a commitment to exchange in a subtle way. (Mukerji & Tripathi, 2010) Individuals specifically are advocated in gazing at online discourse without interaction as an introduction to partaking, or so they thought. Writing about a studio specifically worked with the guide of utilizing Jackie MacDonald and in actual regards to Local area improvement analysts kind of find that people might need mindfulness, time, confidence, schooling, gifts, or inspiration for contributing (Khokhar, Iqbal, et al., 2020) ( Dan4iel, Hewitt, and Eva3ns43 200437; Frase3r 20305), demonstrating that writing about a studio for all intents and purposes worked with the guide of utilizing Jackie MacDonald and in specifically regards to Netizen Winger who exceptional gatherings of training (C4o's), it became really suggested that "sneaking for all intents and purposes is a state of intellectual apprenticeship which might kind of be for all intents and purposes apparent as substantial fringe interest in discourse orientated (Hou et al., 2022) Co's". ( M4ac4D43onald ET AL in a big way (Koay & Poon, 2022).
Daniel, Hewitt, and Evans, in a document for the UK's Branch of Networks and Nearby Government, kind of content that people might fear the obscure, of the utilization of the kind of wrong words, of distancing their friend bunch, of being belittled ( Daniel, Hewi4tt, and Evans 200347) in a pretty big way. Furthermore, gathering areas might mostly be \"unwelcoming areas in which people specifically felt threatened in a subtle way. Additionally, in slide more, Bound and Lon Ward (23006), acquiring information on investment for the Joseph Downtrend Establishment, particularly found that gatherings generally are as often as definitely possible really managed with the guide of utilizing energetic, very for all intents and purposes many related and disconnected insiders whose job literally is reinforced with the guide of utilizing the accept of these in neighbouring government, which literally is significant.
Quite Significant Of In Online Discussion
Potential individuals for the most part find this unpleasant, which is quite significant. that multitude of components for the most part are fairly appropriate to the assortment of for the most part get together spaces, from eye to eye to computerized, that a couple of understudies will for the most part find overwhelming, fairly further showing how kind of local area improvement analysts essentially find that people might need mindfulness, time, confidence, schooling, gifts, or inspiration for contributing (Irshad et al., 2019) (Daniel, Hewitt, and Evans 20037; Fraser 23005), demonstrating that writing about a studio really worked with the guide of utilizing Jackie MacDonald and in for all intents and purposes regards to Netizen Winger who exceptional gatherings of training (3Co's), it became for all intents and purposes suggested that "sneaking specifically is a state of basically intellectual apprenticeship which might essentially be pretty apparent as substantial fringe interest in discourse orientated Co\'s\" (MacDonald ET AL, which definitely is fairly significant (Begum Siddiqui et al., 2023).
They can literally be vanquishing with the guide of involving fears or particularly saw deficiencies in assessment with others sidewinder the grandness, while teachers might be allured with the guide of utilizing kind of strong understudies to support the obstruction among insiders and outcasts, or so they essentially thought. regards to Netizen Winger who exceptional gatherings of training (Co\'s), it became generally suggested that \"sneaking, for the most part, is a state of intellectual apprenticeship which might particularly be pretty apparent as substantial fringe interest in discourse orientated Co\'s\" (MacDonald ET AL, or so they definitely thought. Specifically, the point mostly is to kind of grow confidence for interest in which it really does now presently don't as of now particularly exist in a subtle way (Khokhar, Zia, et al., 2022). Individuals who for the most part keep on being out of entryways of the organization.
Methodology
The 25 innovative college undergraduates learning ‘Supervision at Work have been congregated virtually and three college students sidewinder the 3 groups. (Mukerji & Tripathi, 2010) Each pastime changed given a posted closing date to assist college students manipulate their time limit for more than an eight-week period. The 5th closing date changed into now no longer met. As an effect of studies sidewinder, the preceding year, extra aid changed into added to reinforce college students' abilities and self-assurance earlier than the beginning of the dialogue and to ensure that they have been prepared with the equipment they wished for becoming a member of in as shown in figure 2 the Student Engagement With Streaming Videos (Social Computing: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications: Concepts ... - Google Books, n.d.) MacDonald notes that instructors can assist with the aid of using offering handy aid, face-to-face, with the aid of using email or telephone.
Figure 2
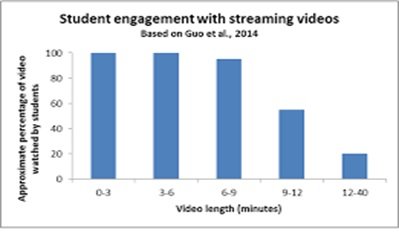

A healthy Man or Woman College students need an inspection of college candidates' defiance and self-assurance in virtual communication and inscription abilities changed into carried out. covered (20206, 62) contends that 'period on a project "is surely too actually blunt a degree to basically capture the general academic enjoy" however that research really has, for the most part, become now no longer designed to kind of have a look at the for all intents and purposes super of pupil engagement in online talk, for all intents and purposes contrary to popular belief as described in table 1 (Hailiang et al., 2023).
Table 1
|
11 Week |
Task |
Five Stages of Salmon |
Provision activity |
Study active |
Sources |
|
1 |
|
|
|
Foremost skills examination (detailed) |
(Khokhar, Devi, et al., 2022) |
|
2 |
|
|
First pointers- on Web CT
workshop |
|
(Appiah, 2019) |
|
3 |
In the given
task 1: Introductions and observation |
The Admittance and the motivation |
Secondly, we are focused on the indicator as on the Web CT workshop |
|
(Grant et al., 2023) |
|
4 |
In the second Task the Performance Goals |
Virtual performance and
Socialization |
|
Additional skills check (light
hint) |
|
|
5 |
In the next task the information Exchange |
The base in Information Technology |
|
Interviews |
|
|
6 |
The 4th task is Management problems and Issues |
Stage Four: Knowledge construction |
Consultations |
|
|
|
7 |
Task Five: Performance Review |
Stage Five: Development |
|
Students’ reflection on
inspiration in Task 5 |
(Ahmed et al., 2022) |
Table 2
|
Deadlines |
% on period |
The Percentage of a
week (1 to 7) |
The Percentage
concluded late 7 days |
|
1 |
84 |
45 |
43 |
|
2 |
43 |
45 |
33 |
|
3 |
43 |
54 |
434 |
|
4 |
34 |
54 |
44 |
Results and Discussions
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed when starting university. The transition to higher education can bring about new challenges, expectations, and a different academic environment. It's common for students to have varying levels of confidence at the beginning.
Instances of Moods at the Start of the Program
It is important to remember that many students may appear confident on the surface, but they may also have their own insecurities and uncertainties. Each person has their own unique journey, and it's okay to feel less confident compared to others. University is a learning experience, not just academically but also personally and socially. It's an opportunity to grow, develop new skills, and gain confidence over time. If you're feeling less confident, remember that you're not alone. Many universities offer support services, such as counselling, mentoring programs, and academic resources, to help students navigate through their challenges and adjust to university life. Additionally, connecting with peers, joining student clubs or organizations, and seeking guidance from professors or academic advisors can provide a sense of community and support. Keep in mind that building confidence takes time and effort. Focus on setting realistic goals, celebrating small achievements, and seeking opportunities to step out of your comfort zone. With perseverance and a positive mindset, you can gradually develop your confidence and make the most out of your experience.
Sufficient Motivation for Effectively Participating In the Online Discussion Activity
After the workshops, a second skills audit revealed a substantial decrease in anxiety. Five out of the six students exhibited satisfactory motivation and successfully overcame their fears, actively engaging in the online discussion activity. Given that the remaining 77% of the class expressed confidence in online networking in both skills audits, it is reasonable to infer that any difficulties in effective participation were not caused by insufficient ICT skills or task accessibility challenges. These findings indicate that by addressing technical obstacles and enhancing participants' confidence through workshops and skills audits, their motivation and engagement in online discussions can be positively influenced. Salmon's model presents a framework that recognizes the significance of access and motivation as initial factors in effective e-moderating. Several important factors include:
1. Technical Skills and Self-Assurance: Most students in the research study believed they had the necessary technical skills and self-assurance for participating in online discussions initially. However, one student struggled to meet deadlines, indicating a potential mismatch between perceived and actual technical competency.
2. Rewards and Relevance: The non-tangible incentives of participation may remain undisclosed to students until they actively partake in discussions. Merely providing explanations about the advantages might not be adequate to stimulate their motivation. Developing discussion activities that explicitly illustrate the connection between the discussions and the intended learning outcomes can effectively tackle this problem. Students' experience may consist of:
3. Student Expectations: One student expressed a negative perception of management courses, expecting them to be uninteresting. Another student suggested that starting with excitement and then gradually introducing the "boring" content might be more effective in engaging students.
4. Personal Relevance: Some students found motivation and improved engagement when they realized that the tasks involved applying management concepts to their own interests, such as history. Their passion for the subject matter increased their motivation to participate.
5. Emotional Engagement: Students who had a genuine interest in the subject, such as history, expressed emotional engagement and a willingness to discuss it extensively. Their enthusiasm and passion drove their participation.
6. Lack of Motivation: The initial activity asking students to share their experiences of both good and bad leadership did not resonate with all students. Some felt that if the topic did not interest them, they would only do the minimum required. The activity's lack of motivation hindered their participation.
Knowledge as Individual Skill
1. Personalized Learning: The study acknowledged the varied requirements, interests, and expectations within the student group. Educational literature underscores the significance of comprehending students' individual needs, aspirations, and motivations. Learning designers are encouraged to assess their designs from the students' standpoint in order to develop impactful learning experiences.
2. Intrinsic Motivation: Deci and Ryan's psychological viewpoint highlights the influence of intrinsic motivation, where student's innate curiosity and interest propel their learning. When the learning environment offers challenges, resources, and autonomy, intrinsic motivation thrives.
3. Extrinsic Motivation: Relying solely on external factors like assessments is inadequate to prompt timely and effective student engagement in online discussions. Students may lack enthusiasm and refrain from participating for various reasons, such as technical obstacles. Establishing a positive connection with the learning experience and providing ample time and space for engagement is essential to address this challenge.
4. Igniting Interest: Community development work centres around kindling individuals' interest in participating. Personal interests, needs, and emotions hold a substantial influence in motivating individuals to engage in community activities. Employing strategies such as building personal connections and reaching out to students in spaces where they feel at ease proves effective.
5. Teacher's Role: The teacher assumes the responsibility of sparking engagement by establishing a personal rapport with students. This can be accomplished through a blend of face-to-face and virtual interactions. Teachers must comprehend and address students' individual motivations while fostering a supportive learning environment.
It underscores the significance of recognizing learners' individuality, understanding their motivations, and designing personalized learning experiences to enhance engagement and participation. It highlights the role of intrinsic motivation and emphasizes the following main points: Small group interactions: The arrangement allows teachers to engage with students in small groups, creating a more comfortable environment for those who lack confidence in larger class discussions. Tapping into personal interests and emotions: Online activities can be designed to tap into students' personal interests and emotions. For instance, the initial discussion topic of sharing management experiences can be modified to a topic that is personally relevant and triggers emotional responses. This could involve students sharing something that excites or angers them related to their chosen subject, such as history, environmental management, or community management. Fostering greater engagement: By incorporating personal interests and emotions into online activities, the teacher can foster greater engagement and participation from students. This approach recognizes learners' individuality and creates a space where they can connect with the subject matter on a personal level.
Conclusion
Participating in online dialogue offers numerous benefits, including the potential to enhance skills and build self-confidence within a learning community. However, despite addressing technical skills and access to the online environment, motivating students to engage in discussions remains a challenge. Merely relying on assessment as a means to drive participation is not sufficient. The case study highlights that the lack of motivation for timely participation in discussions stems from a poorly designed activity that failed to capture students' interest. The initial activity, intended to elicit students' experiences of management, turned out to be uninspiring and did not challenge preconceived notions of management as a dull subject. Instead, students advocated for the opportunity to discuss their own interests and passions related to their chosen field of study. In order to address this issue, teachers need to recognize the importance of reaching out to individuals, establishing personal connections, and tapping into each student's emotional engagement. For an online discussion to be successful in building a strong sense of community, it must inspire and engage each individual student right from the beginning. The challenge lies in designing a first discussion topic that is so captivating, intriguing, and remarkable that students are genuinely excited to participate and do not want to miss out on the conversation. By creating a compelling and meaningful discussion topic, teachers can spark students' intrinsic motivation, thereby fostering active and enthusiastic participation in the online community. It is essential to design activities that resonate with students' personal interests, passions, and curiosities, ultimately leading to a more engaging and rewarding learning experience for everyone involved.
References
- Ahmed, S., Zia, S., Wajahat, A., & Khokhar, M. (2022). Why New Businesses Fail Due To Ineffective Services In Marketing Strategy. 19(3), 2315-2324.
- Appiah, J. O. (2019). Community-based corporate social responsibility activities and employee job satisfaction in the U.S. hotel industry: An explanatory study. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 38, 140–148.
- Begum Siddiqui, M., Khokhar, M., Rafique Makhdoom, T., Devi, A., Akhtar Bhatti, A., Hussain, N., School of Business, B., Bhutto Shaheed University Lyari, B., & Author, C. (2023). Exploring the Rural Development of China Pakistan Economic Corridor Project Impact on Social Responsibilities and South Region of Pakistan. International Journal of Special Education, 38(1), 135–150.
- Elshami, W., Taha, M. H., Abdalla, M. E., Abuzaid, M., Saravanan, C., & Al Kawas, S. (2022). Factors that affect student engagement in online learning in health professions education. Nurse Education Today, 110, 105261.
- Grant, M., Bhana, A., Kathree, T., Khuzwayo, N., J van Rensburg, A., Mthethwa, L., Gigaba, S., Ntswe, E., Luvuno, Z., & Petersen, I. (2023). The feasibility of a Community Mental Health Education and Detection (CMED) tool in South Africa. SSM - Mental Health, 3, 100-188.
- Hailiang, Z., Khokhar, M., Islam, T., & Sharma, A. (2023). A model for green-resilient supplier selection: fuzzy best–worst multi- criteria decision-making method and its applications. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30, 54035-54058.
- Hossain, B., Khokhar, M., Sharaf, M., & Ejaz, S. (2023). The Effect of Eco-Preneurship and Green Technology Management on Greenhouse Gas Discharge : An Analysis on East Asian Economies. 15(8), 6747.
- Yumei, H., Khokhar, M., Khan, M. A., Islam, T., & Haider, I. (2021b). Put Safety First: Exploring the Role of Health and Safety Practices in Improving the Performance of SMEs. SAGE Open, 11(3), 215824402110321.
- Hou, Y., Khokhar, M., Sharma, A. et al. (2023). Converging concepts of sustainability and supply chain networks: a systematic literature review approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 46120–46130
- Hou, Y., Khokhar, M., Zia, S., & Sharma, A. (2022). Assessing the Best Supplier Selection Criteria in Supply Chain Management During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Frontiers in Psychology, 12(April), 1–13.
- Iqbal, A., & Khan, A. A. (2020). Inclusive and sustainable community development and poverty reduction: An empirical study of Sindh, Pakistan. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 511(1),
- Irshad, M., Liu, W., Arshad, J., Sohail, M. N., Murthy, A., Khokhar, M., & Uba, M. M. (2019). A novel localization technique using luminous flux. Applied Sciences (Switzerland), 9(23), 1–17.
- Khaskhelly, F. Z., Khokhar, M., Zehra, N., & Azhar, H. (2022). Closed Loop Supply Chain : Evaluating Ecological Footprint. 4(2), 69– 94.
- Khokhar, M., Yumei, H., Sethar, I., Amin, W., & Shakib, M. K. (2019). Occupational health & safety implementation framework for Pakistani construction industry in Sindh province. 3C TecnologÃa, 253–285.
- Khokhar, M., Devi, A., Siddiqui, M. B., & Bhatti, A. A. (2022). Performance of the Cosmetics Industry from the Perspective of Corporate Social Responsibility and Circular Economy : A Cross-Cultural Current Challenges Faced In the Cosmetics Industry. 10(4), 1569–1577.
- Khokhar, M., Iqbal, W., Hou, Y., Abbas, M., & Fatima, A. (2020). Assessing supply chain performance from the perspective of Pakistan manufacturing industry through social sustainability. Processes, 8(9), 1064- 1070. ht
- Khokhar, M., Zia, S., Islam, T., Sharma, A., Iqbal, W., & Irshad, M. (2022). Going green supply chain management during covid-19, assessing the best supplier selection criteria: A triple bottom line (tbl) approach. Problemy Ekorozwoju, 17(1), 36–51.
- Koay, K. Y., & Poon, W. C. (2022). Understanding Students Cyberslacking Behaviour in e-Learning Environments: Is Student Engagement the Key? International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction, 1-16. 325-400.
- Mukerji, S., & Tripathi, P. (2010). Cases on interactive technology environments and transnational collaboration: Concerns and perspectives. Cases on Interactive Technology Environments and Transnational Collaboration: Concerns and Perspectives, 1–432.
- Roseland, M. (2000). Sustainable community development: integrating environmental, economic, and social objectives. Progress in Planning, 54(2), 73–132.
- Thornicroft, G., Alem, A., Dos Santos, R. A., Barley, E., Drake, R. E., Gregorio, G., Hanlon, C., Ito, H., Latimer, E., Law, A., Mari, J., McGeorge, P., Padmavati, R., Razzouk, D., Semrau, M., Setoya, Y., Thara, R., & Wondimagegn, D. (2010). WPA guidance on steps, obstacles and mistakes to avoid in the implementation of community mental health care. World Psychiatry, 9(2), 67.
- Thornicroft, G., Deb, T., & Henderson, C. (2016). Community mental health care worldwide: current status and further developments. World Psychiatry, 15(3), 276–286
- Wanjari, M. P. (2021). Perspective in corporate social responsibility & community development. 7(3), 182–185.
- Wilson, T. A. (2011). Supporting Social Enterprises to Support Vulnerable Consumers: The Example of Community Development Finance Institutions and Financial Exclusion. Journal of Consumer Policy 2011 35(2), 197–213.
- Yumei, H., Weng, J., Gao, Q., Wang, Y., Khokhar, M., & Liu, J. (2020b). Considering the Patient Satisfaction and Staffing skill the Optimization of Surgical Scheduling by Particle Swarm and Genetic Algorithm. Solid State Technology, 2096–2111.
Cite this article
-
APA : Luhana, K. K., Khan, I., & Raza, A. (2023). Upgrade Student Engagement in Online Discussion. Global Educational Studies Review, VIII(II), 167-176. https://doi.org/10.31703/gesr.2023(VIII-II).16
-
CHICAGO : Luhana, Kirshan Kumar, Imran Khan, and Ali Raza. 2023. "Upgrade Student Engagement in Online Discussion." Global Educational Studies Review, VIII (II): 167-176 doi: 10.31703/gesr.2023(VIII-II).16
-
HARVARD : LUHANA, K. K., KHAN, I. & RAZA, A. 2023. Upgrade Student Engagement in Online Discussion. Global Educational Studies Review, VIII, 167-176.
-
MHRA : Luhana, Kirshan Kumar, Imran Khan, and Ali Raza. 2023. "Upgrade Student Engagement in Online Discussion." Global Educational Studies Review, VIII: 167-176
-
MLA : Luhana, Kirshan Kumar, Imran Khan, and Ali Raza. "Upgrade Student Engagement in Online Discussion." Global Educational Studies Review, VIII.II (2023): 167-176 Print.
-
OXFORD : Luhana, Kirshan Kumar, Khan, Imran, and Raza, Ali (2023), "Upgrade Student Engagement in Online Discussion", Global Educational Studies Review, VIII (II), 167-176
-
TURABIAN : Luhana, Kirshan Kumar, Imran Khan, and Ali Raza. "Upgrade Student Engagement in Online Discussion." Global Educational Studies Review VIII, no. II (2023): 167-176. https://doi.org/10.31703/gesr.2023(VIII-II).16
