Abstract
This study probes the socio-economic and school background factors that may affect students' marks in primary schools in northern Pakistan. The data was collected from four parts of the province. The result confirms that free lunch is an influential academic booster if provided to lower groups of students; in some cases, the school is away from students. Adequate staff and adequate funds, too, have elevating effects on marks. Male parents are a means of more academic gain for male students and less for females. Internet at home is a better option. Recommendations are delineated at the end.
Key Words
Education, Evaluation, Gender, Economics Public Finance, Public Policy
JEL Classification:
H52, I21, H75
Introduction
Education has been a well-discussed subject of social development. The purpose of education is to learn to spend life in a better way, and better grades are supposed to weigh the quality of this ability. It is assumed that the grades are dependent on various factors from school to student background. Schooling that aims for a universal ‘state-funded system is more valued, implying that less costly private schools are no longer needed (Siddiqui and Gorard 2017). Also, the individual intelligence quotient does have an influence, but other factors are equally important.
There are dependencies on some inputs, in form and processes for each level, and their association with performance to accomplish various achievements (OECD 2005). For instance, there is a perception that students belonging to non-metropolitan locations have low academic performance (outcomes) and retention rates compared to metropolitan students (Cheers 1990; Human Rights and Equal Opportunity Commission 2000). According to (Chandrasekhar and Mukhopadhyay 2006), indirect and direct costs are prominent in affecting school attendance, but other factors also affect a hundred per cent of primary enrollments in India. Gender, opportunity cost, and attitude are some of them. They also state that the effect of costs on a boy's education differs from a girl's education and the effect of direct costs on a girl's education is substantial. Later on, (Vavrus and Moshi 2009) also discussed the effect of cost and domestic work obligation in defining girls' education enrollment and continuity. It was revealed that abolishing school fees is not a panacea for universal primary education but the total cost of education at that level. It has been a concern for many parents in observation. Studies related to factors affecting students' performance can guide policymakers in devising an effective mechanism for improving the status quo.
According to (“| Ministry of Finance | Government of Pakistan |” n.d.) GoP (2021), the literacy rate of Pakistan remained sluggish at a rate of 60% from 2014-2-015 to 2019-2020. The collective expenditure of the federal and provincial governments was 1.5% of GDP in 2020 against 2.3% of GDP in 2019. Figure 1 shows a decreasing trend in education spending in the past few years. There was also (figure 1) negative annual change for almost a decade from 2008 to 2014.
Figure A
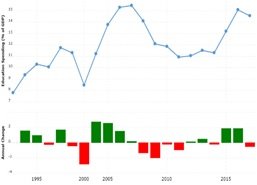
The negligence of the authorities to invest in education has detrimental effects on the state of primary-level education in the country. (Batool and Webber 2018) found that students from private trusts, government primary schools, and unregistered schools could not comprehend (present, organize, and use the provided information) hence lacking basic skills. On the other hand, the economically better class exhibited better, and the school's poor conditions could result in dropouts. These may include physical characteristics, social family-related factors, teaching methods, and quality, teaching material, administrative features, and child-self issues (Shah, Haider, and Taj 2019). There are geographical differences as well. Parents, too, are not spending alike on all children (Jehan and Idris 2019).
The gender aspect of educational attainment and performance has been researched for years (Eitle 2005), and it is evident that girls perform better than boys in various cases (Chambers* and Schreiber 2004) quality of the performance of the students has also been prioritized (Crosnoe, Johnson, and Elder Jr 2004). In some instances, it is shown that education has been taken as a feminine effort while working is a masculine activity (Jha and Kelleher 2006)
Decisions about education must be gender specific. Researchers like (McCoy 2005) and (Peng 1995) consider gender a contributor to student advancement. So, it is evident that achievements in an academic sense are also gender-based, and factors may affect both genders differently. (Jehan and Idris 2019) also show a difference in the background cost of female education and male education; hence, a differential effect may be expected.
According to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, approved in 1948, education was recognized as the right of every human, and Article 26 also added compulsion to secondary education. The sustainable development goals set by United Nations urge the world to ascertain free and equitable primary and secondary education till 2030. Nevertheless, the gender effect is vital in attaining education, and girls are most disadvantaged regarding quality education (G n.d.). Literature, to the known knowledge of the author, somehow fails to give an empirical estimation (econometric) of the mix factors, including cost factors, background factors, and school factors presented in this research.
There is ample research on students outcomes in higher education (Goss 2022; Renn and Reason 2023), or focused on teachers' attributes like empathy (Aldrup, Carstensen, and Klusmann 2022), there have been context-specific studies like health care (Ryan et al. 2022), instrumental quality and teachers exhaustion(Klusmann et al. 2022), focus on science class
Research relate to primary education focuses on reading interest and learning (Yunita and Komsi 2023), development of computational skills (Vourletsis and Politis 2022), distance teaching(Panskyi et al. 2022), virtual realities (Villena-Taranilla et al. 2022), learning centred pedagogy (Bremner, Sakata, and Cameron 2022), school-based universal mental health programs(Cefai et al. 2022), consequences of school closure (Maldonado and De Witte 2022),
This research addresses the students' background and school background factors affecting high performance at government primary-level institutions in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. The study is unique because it focuses not on students but on surrounding situations. Not IQ but the contextual variables. The education system is supposed to be free, but other factors besides tuition fees are ignored; hence, education is not freely available in the true sense. The term user fee thus affects academic achievements (Kaguamba 2011) which can lead to adverse effects (Ubogu 2004). So, we tried to answer the following questions in our study:
RQ1: Do students' contextual factors affect their academic performance (marks)?
RQ2: Is there any effect of school contextual factors on a student's percentage marks?
To answer these questions, the researcher has followed a comprehensive sampling procedure. Data was collected through questionnaires and interview schedules, and we used STATA software. The analysis was done for the percentage outcomes of the student as the dependent variable and other background factors as independent variables. The study starts with the background of the study, and the literature review, followed by the sampling and estimation methods. The results are interpreted and discussed, followed by a conclusion and policy recommendations.
Literature Review
Literature related to student outcomes is rich, and studies from different perspectives are evidence of this. In 2003, the EFA global monitoring report referred to the emergence of skewed trends toward girls, both from performance and participation perspectives (Unterhalter 2003). This rhetoric is again approved by (Fiske 2012) that in some developing countries, girls outperform boys in academic achievement and further progression. Gender differences in achievements are negligible if the girl student is disadvantaged concerning access to education (Chege 2007). The trend of girls' performance was observed in Kenya (Lucianne, 2013) when girls secured the top seven positions in Kenya Certificate of Primary Education (KCPE) tests. In connection to this, boys may be adaptive to the disruptive behaviour of their peers, and their attention is diverted to status gains, not academic gains. In developing countries, a stigma is associated with studious male students as the study is considered a feminine activity (Legewie and DiPrete 2012) and we can assert that the guardian's gender may affect students' achievements (Millette 1988). Socio-economic factors determine the percentage of academic achievements because of their inherent relationship with the need fulfilment of students (Adams 1996).
(Simon 1980) argued that the effect of students' background and their parents ‘status (social and economic) is comparatively prominent at primary and low secondary levels compared to variables controlled by school policies. They also confirm that these results are the same across developing and developed countries. Earlier, (Reid 1983) work addressed the same issue: the independent effect of school factors or their combination with community variables. Another study by (Saha 1983) and (Avalos and Haddad 1979) shows that student performance has been significantly affected by the teacher and school variables.
Studies by (Farooq et al. 2011; Rahman and Uddin 2009) agreed on the positive effect of parent education on students' grades in inner-city territories of Pakistan. (Habibullah and Ashraf 2013) showed that Pakistani children from low socio-economic backgrounds achieve good grades. Their study confirms a positive relationship between school/classroom conditions and students' grades. The results revealed that girls show higher marks than boys, and sports activities are associated with good grades. In 2013, the then government initiated various reforms to attain universal primary education. According to the United resolution, education is free at the primary level. However, students' academic gains can be affected by many things, and the effect of some other factors besides school fees cannot be overlooked.
Individual differences like the Intelligence Quotient level remain one of the most significant factors towards students' achievements. It is evident from the literature that individual student achievement is highly related to intelligence (from r=.3 to r=0.7) (Brody 1997; Gustafsson and Undheim 1996; Sattler and Ryan 2009; Chamorro-Premuzic, Quiroga, and Colom 2009; Colom and Flores-Mendoza 2007; Deary et al. 2007; Gottfredson 2002; Jensen 1998; Kuncel, Hezlett, and Ones 2004; Kyttälä and Lehto 2008; Laidra, Pullmann, and Allik 2007; Lemos et al. 2014; Neisser et al. 1996; Primi, Ferrão, and Almeida 2010; Rosander, Bäckström, and Stenberg 2011; Taub et al. 2008; Agarwal et al. 2021). (Agarwal et al. 2021) specifically targeted this fact and found that intelligence is significantly related to academic achievements. In another study, (Bruni et al. 2006) added demographic and psychological factors to study their effect on the academic outcome, but not the intelligence quotient. In a parallel connection, (Deary et al. 2007) concluded that intelligence has a strong positive relationship with academic outcomes. Hence intelligence tests/quotients are very influencing factors for individual academic achievements. So, studies related to determinants of student outcomes must not overlook this relation. In the present study, IQ level was not included because IQ was not calculated earlier, nor was it the scope of the study. Hence, factors other than IQ are taken as independent variables.
In a study by (Liu, Peng, and Luo 2020), socioeconomic status (SES) had a moderate effect on academic performance. This meta-analysis for China shows that the relationship between SES and academic achievements decreases with time. The SES did not prove significant in grade-level estimations. Lower grades are sometimes related to lower SES (Ruiz, McMahon, and Jason 2018). Among other socio-economic variables, the education and occupation of parents are the key factors that affect results (Taylor 2018; Ilie, Sutherland, and Vignoles 2017). Some studies suggest that teaching competence (quality) is also responsible for student outcomes (Hanushek and Woessmann 2017). A study by (Liouaeddine, Bijou, and Naji 2018) shows that not only individual but contextual factors also affect students' performance in Morrocco. Though there are agreements that SES affects a student's grade, there is no clarity about the
mechanism of effect (Thomson 2018).
We can conclude that students' background, of which socio-economic background is most prominent, acts significantly on their academic achievements. There are gender differences, and parental education is also considered adequate. Parent gender is not included in previous studies, which in the discussed context is expected to have some effect, so we included it in the study. As no such study is carried out in the Pakistani context, we have tried to fill this gap, considering the discussed variables. We have included teachers' satisfaction and the personal administrative needs of each school as well. In totality, the background variables and school background (contextual) variables are included. This positioning gives a unique edge to this study.
Methodology
All school statistics are taken from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa's official education website. According to the information, 71 per cent of the schools are run by the KP government. There are 17 per cent non-government schools and 12 per cent madrassa schools. Our study aims at costing out government-run schools' needs so that we focus on 71 % of the schools. Non-government schools cannot be considered fit for study as they are run for profit; there, education is treated as a business. As madrassa is not a formalized setup, and there are variations in curriculum and style of studying among them, therefore they are excluded from the study. The primary level has a maximum number of schools (81%), and most resources are needed there.
The schools are further divided into urban and rural schools with gender specifications. There are areas where urban schools are very few compared to rural schools because their setup is rural. Most of the districts of KP are rural. There is another reason, the urban setup has been concentrated with many non-Governmental schools, and rural areas are District Kohistan is a rural area and is mainly served by government schools. There is not a single urban school because the area is rural. Shangla and Torghar are similar cases. Buner and Battagram, too, have only one girl and one boy school in an urban location. Dir Bala, Karak, and Tank also have very few urban schools. There are plain areas in KP like Charsadda, Peshawar, Nowshehra, Mardan, Swabi, Kohat, and DI. Khan lies in plain but has many urban schools. The stratification was applied while keeping in view all these facts.
Sampling Technique
Stratification
The sampling technique is applied to select a representative sample for fulfilling project objectives. The study applied the stratification process in the first step. Care was taken to select those districts in one mutually exclusive group with similar circumstances. We divided our sample districts into four strata. From each stratum, a district was randomly selected. The final selected districts are given in Table 1.
Table 1
|
District Name |
Urban schools |
Rural schools |
||
|
|
Boys |
Girls |
Boys |
Girls |
|
Karak |
9 |
12 |
428 |
324 |
|
Shangla |
0 |
0 |
436 |
166 |
|
Mardan |
82 |
56 |
746 |
564 |
|
Haripur |
22 |
15 |
543 |
344 |
|
Total |
113 |
83 |
2153 |
1398 |
Table 2
|
District Name |
Urban
schools |
Rural schools |
||
|
|
Boys |
Girls |
Boys |
Girls |
|
Karak |
9 |
12 |
428 |
324 |
|
Shangla |
0 |
0 |
436 |
166 |
|
Mardan |
82 |
56 |
746 |
564 |
|
Haripur |
22 |
15 |
543 |
344 |
|
Total |
113 |
83 |
2153 |
1398 |
|
Sample |
88 |
69 |
337 |
311 |
Table 3
|
District Name |
Urban schools |
Rural schools |
||
|
|
Boys |
Girls |
Boys |
Girls |
|
Karak |
7 |
10 |
66 |
72 |
|
Shangla |
0 |
0 |
68 |
37 |
|
Mardan |
64 |
47 |
116 |
125 |
|
Haripur |
17 |
12 |
85 |
76 |
|
Total |
88 |
69 |
335 |
310 |
Conceptual Framework
Numerous studies have shown the relation of student achievement as a dependent variable compared to other independent variables. Among them, (Simon 1980) discusses that the effect of students' background and their parents 'status (social and economic) is comparatively prominent at primary and low-secondary levels. (Gorman and Pollitt 1996) shows that socio-economic variables are detrimental to students' achievements, as shown in the earlier result by (Millette 1988), who finds the effect of parent gender on student achievements. Before these studies, (Reed 1976) addressed the collective effect of school and community variables on student outcomes. At the same time, (Saha 1983) and (Avalos and Haddad 1979) find the influence of school and teacher-related variables on a student's academic outcome. In Pakistan, (Farooq et al. 2011) show the significant effect of parent education and socioeconomic factors, which is confirmed by (Habibullah and Ashraf 2013) that students belonging to low socio-economic backgrounds in inner cities of Pakistan are good achievers. (Rahman and Uddin 2009) also confirmed the strong effect of parent education and father/guardian income on students' educational achievements in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.
The following conceptual model is developed while keeping in mind the variables included in other studies.
Outcome = f (location, student gender, guard gender, distance (km), salary head, free lunch, proper fund, staff adequacy, socialgrp1, socialgrp2, head education, Total Cost, Electricity bill, salary satisfied, internet, single class teacher, school strength, admin staff)
We also included interaction terms in the above model: Free lunch and social group 1, free lunch and social group 2.
Or
Op = f (L, StG, GG, D, SH, FL, PF, SA, SG2, SG3, HE, TC, EB, SS, St, AS, SCT, In) ------- (1)
Where:
Op refers to an outcome, the percentage result of a student in a previous examination.
L refers to a location. Urban location is represented by 1 and rural as 0.
StG refers to student gender, with a male student coded as 1 and a female as 0.
GG to guard gender and is one if the guard is male and 0 otherwise.
D shows the distance from the child's home to the school, measured in KM.
SH refers to the heads salary/earnings per month,
PF shows proper funds, and if the proper fund is lacking, it is coded as 1 and zero and vice versa.
FL will be one if free lunch is provided in the school and “0” otherwise.
SA refers to staff adequacy, it is a dummy, and no staff adequacy is coded as 1 and 0 otherwise.
SG2 is used for social groups. It is a dummy; if a person belongs to the middle class, then the case is coded as 1 and all others as 0.
SG3 is used for social groups. It is a dummy; if a person belongs to the upper class, then the case is coded as 1 and all others as 0.
EB shows the electricity bill in rupees.
SS shows salary satisfied teacher and is coded as 1 and 0 and vice versa.
HE: indicates the education level of the head of the family. Suppose a person is literate=1 and 0 otherwise.
TC refers to the total cost of a student besides tuition, including stationery, uniform, and daily pocket money. All the costs were indexed into the daily cost.
Interactions: Free lunch with social groups (SG2 & SG3)
AS: is the number of administrative staff.
St: It shows the number of students in the school
ST refers to Single class teacher
It shows the presence and use of the internet at home.
(L, StG,GG,D,SH,FL,PF,SA,SG1,SG2,HE,TC, EB, SS, St, AS, SCT, In)
The above equation after estimation becomes:
O=?+?_1 L+?_2 StG+?_3 GG+?_4 D+?_5 SH+?_6 FL+?_7 PF+?_(8 ) SA+?_9 SG2+?_10 SG3+?_11 HE+?_12 TC+?_13 EB+?_14 SS+?_15 St+?_16 AS++?_16 SCT+?_17 In+?_17 ST? …..(4)
Interactions were added to the equation, including a social group of the middle class and free lunch, a group of the middle class, free lunch, and distance, a group of the upper class and free lunch, a social group of the upper class, distance, and free lunch, respectively. The equation becomes:
O=?+?_1 L+?_2 StG+?_3 GG+?_4 D+?_5 SH+?_6 FL+?_7 PF+?_(8 ) SA+?_9 SG2+?_10 SG3+?_11 HE+?_12 TC+?_13 EB+?_14 SS+?_15 St+?_16 AS++?_16 SCT+?_17 In+?_18 SG2_FL+?_19 SG2_FL_D+?_18 SG3_(?_?) FL+?_18 SG3_FL_D …..(5)
Results and Discussion
Coefficients Comparison of Regression Estimations
The results of the analysis are presented in Table 4. We have estimated the results in four distinct manners. The first column is the estimated results of the main sample, consisting of male and female students. The second column is the results for female students only, and the third is for males. The fourth column consists of the main sample with interactions. The main aim is to compare the explanatory power of independent variables across dependent variables for these samples. The first row, which represents the effect of location, shows a clear hint that whether a student belongs to a rural or an urban area, and it does not affect the percentage marks achieved by a male or female student. However, if we look at the second row, the gender of the guardian of a student has a different influence on a male student than a female student. As a girl student, the father as guardian (here guardian is represented as the one in parents/family who frequently goes to child school and most of the communication is directed towards him/her) is exerting negative pressure on her marks. The coefficient for the overall sample is insignificant in both interaction and non-interaction cases. A male guardian has a reverse effect on a girl student- almost four marks decrease in her final percentage. Now it seems somewhat plausible. The society we live in Northern Pakistan is exerting pressure on a girl who is going to school. It is a huge favour to her. She is not supposed to be the bread earner and, in most cases, is considered married soon. The visits and influence of a male guardian no doubt pressure her, and this fear may have an adverse effect. We presume the result is entirely consistent because of the low standard error.
On the contrary, the male guardians' regression coefficient is positive for male students, and it is statistically significant and almost doubles, i.e. 8.13 of the same for the girl students. The result is a depiction of our attitude toward a male student. We can say that the boy students feel valued or are motivated to work hard when their guardian is male. The child's male guardian visits most male schools; however, in some instances, females do the duty. A male guardian can easily interact with male teachers.
In contrast, a male guardian cannot easily visit a female school, which is why the girl child may feel pressurized, and it is also considered harmful if a male guardian contacts a female teacher. Another explanation for the result is that the father is considered great support and a protective element in society. A female guardian hardly controls male students and sometimes gets spoiled without a male guardian. The presence of a guardian is a new variable that we have added to the model and proved very significant.
Table 4
|
Students Background |
||||
|
Student percentage |
Main Sample |
Girls only |
Boys only |
With interaction |
|
Location |
-0.265 (0.75) |
1.16 (1.46) |
-0.15(0.88) |
-1.26*(0.64) |
|
Guardian gender |
-0.683 (1.31) |
-4.15* (1.49) |
8.13* (3.18) |
-2.44*(1.18) |
|
Internet |
2.401* (1.03) |
2.73** (1.55) |
1.98 (1.75) |
1.29(1.15) |
|
Student Gender |
0.415
(0.80) |
---------------- |
--------------- |
-0.42(0.77) |
|
Salary head |
0.000* (0.00) |
-0.00* (0.00) |
-0.00* (0.00) |
-0.00*(0.00) |
|
SG2 |
-2.347* (1.06) |
-4.22* (1.33) |
-0.98 (1.74) |
-3.81*(1.18) |
|
SG3 |
-0.055 (1.32) |
-5.33* (2.31) |
2.19 (1.59) |
-0.91(1.39) |
|
Head education |
-1.477 (0.10) |
-3.65 (1.57) |
-0.99 (1.45) |
4.30(2.89) |
|
School Background |
||||
|
Proper fund |
-0.183 (0.18) |
-1.75 (1.50) |
-0.19 (0.16) |
-4.87*(1.07) |
|
Electricity bill |
0.001* (0.00) |
0.00* (0.00) |
0.00* (0.00) |
0.00(0.00) |
|
Salary satisfied |
2.638* (1.34) |
5.07 * (2.08) |
2.66 (1.80) |
3.52(1.31)* |
|
TC |
0.000 (0.00) |
0.00 (0.00) |
0.00 (0.00) |
0.00* (0.00) |
|
School Strength |
0.019* (0.00) |
0.02* (0.00) |
0.02* (0.01) |
0.013*(0.002) |
|
Distance(km) |
0.515 (0.31) |
0.72* (0.33) |
0.26 (0.51) |
0.52(0.29) |
|
Single class teacher |
1.092* (0.00) |
-0.11 (0.75) |
1.06* (0.50) |
0.71*(0.29) |
|
Staff adequacy |
-3.97*(1.023) |
-5.28* (1.65) |
-2.69 (0.00) |
-4.18*(1.01) |
|
Admin staff |
-0.742 (0.27) |
-2.086* (0.47) |
-0.75 (0.60) |
0.72*(0.28) |
|
Free lunch |
-3.543* (1.097) |
-6.61* (1.81) |
-0.98 (1.48) |
-12.61*(2.94) |
|
_cons |
69.491* (0.00) |
77.11* (2.52) |
59.68* (2.93) |
72.45* (1.76) |
|
Interactions |
||||
|
Freelunch_SG2 Freelunch_SG3 Freelunch_distancekm
Freelunch_SG2_dsitance SG2_distance SG3_distance Freelunch_SC3_dsitance
F-value R-squared |
----------- ---------- ----------- ----------- ----------- ----------- -----------
21.20* 0.271 |
------------ ------------ ------------ ------------ ------------ ------------ ------------
11.38* 0.2859 |
---------- ---------- ----------- ----------- ----------- ----------- -----------
57.73* 0.3634 |
13.57*(3.81) 10.24(9.92) 4.42*(1.22) -3.52*(1.62) -0.84(0.87) -2.75*(1.07) -2.236(3.15)
19.25* 0.344 |
|
Root MSE |
9.269 |
9.4972 |
8.4929 |
8.52 |
Figure 1
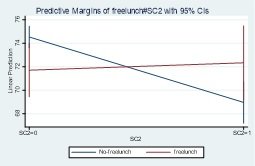
Figure 2

Interaction of Middle Class and Freelunc
The Figure shows the interaction between free lunch, social group belonging to the middle class, and increasing distance, which is statistically significant, with a negative coefficient of 3.52. it clearly shows a decreasing trend for middle-class students' marks gaining. The red line (free lunch) is above the blue line (no free lunch), but the estimated marks are still decreasing. In the present study, the reference category is the lower and lower-middle social class (496 observations are above 77 observations, as shown in Figure 4). Therefore, it is inferred that if a school is at a distance from lower and lower-middle-class students, the availability of free lunch enhances academic gain. Free lunch, however, individually in interaction with the middle class has a very prominent effect of 13.57 marks, and free lunch with the interaction of distance has an increase of 4.42 marks; hence, free lunch is a good idea for primary schools.
Figure 3

Conclusion
This research aimed to find important contextual factors affecting a student's academic achievement. The study did not take any variable that measures a student's IQ or his remarkable ability as the independent variable. Our main aim is to see what other factors affect a student's academic efforts. We have arrived at certain conclusions based on the results. A male guardian has a very significant and elevating effect on a male student's percentage marks, but it has a decreasing effect on the marks of a female student. The distance of the school from the student's home can have a slightly increasing effect on a female, but the effect is not significant as a whole. Although previous research signified the gender effect, we could not find any significant effect of gender on the marks of a student. The use of electricity, which has a significant effect on all students, the impact is less. However, it could be deduced that electricity and amenities motivate students to work hard. The salary of the head of the family has significant but significantly less effective. Researchers have pointed to the effect of social class on students' marks, which has different results.
Students belonging to both the upper and middle classes have significantly fewer marks. Girls, particularly, have lesser marks if they hail from the middle or upper class. Although the literature suggests the effect of the education of a family's head, we could not conclude that it significantly affects a student's percentage marks. The availability of the internet at home increases a girl's student marks. So there is a mixed response of variables belonging to student background. The school background factors have a similar effect. For instance, the availability of free lunch has a decreasing effect on students' and especially girl students' marks; however, the interaction of middle class and free lunch gave a highly elevating effect, and hence we conclude that middle-class students with the provision can have greater academic achievements than other students. The increased strength of students in the school can effectively improve students' academic attainment.
Similarly, an increased number of teachers teaching a single class is better than a single-class teacher, and it positively affects students' marks. Lack of staff adequacy and the need for administrative staff negatively affect a student's academic outcome. An essential fact that we probed was the satisfaction of staff with their salaries which significantly positively influenced the marks of students and girls in particular. We conclude that students' academic achievements depend on their Intelligence Quotient and other factors about their family and school background. The interaction result has brought us to conclude that free lunch suits lower, lower middle and middle social group students. The decreasing effect of distance can be minimized by offering free lunch; however, building schools away from students is still not desirable.
Recommendations
1. The male guardian must visit or supervise a male student while the female guardian should supervise a female student.
2. Amenities like electricity should be provided to each school, and it must be used for students' benefit.
3. A single class must be provided with different teachers for different subjects.
4. Adequate staff should be provided at each school, and there must also be fewer administrative staff in primary schools.
5. The availability of free lunch for students is highly recommended for economically weak students.
6. Teachers' salaries must be fixed according to prevailing inflation.
7. Parents should provide internet facilities to their children at home.
References
- Agarwal, P. K., Zheng, Q., Yang, P. H., Shi, L., Rajadurai, V. S., Khoo, P. C., Quek, B. H., & Daniel, L. M. (2021). Academic school readiness in children born very preterm and associated risk factors. Early Human Development, 155, 105325.
- Aldrup, K., Carstensen, B., & Klusmann, U. (2022). Is Empathy the Key to Effective Teaching? A Systematic Review of Its Association with Teacher-Student Interactions and Student Outcomes. Educational Psychology Review, 34.
- Avalos, B., & Haddad, W. (1981). Review of teacher effectiveness research in Africa, India, Latin America, Middle East, Malaysia, Philippines, and Thailand: Synthesis of results.
- Batool, S. H., & Webber, S. (2018). A contextual framework for primary education: fostering information literacy in Pakistan. Global Knowledge, Memory and Communication. 68(3), 164–76.
- Bremner, N., Sakata, N., & Cameron, L. (2022). The outcomes of learner-centred pedagogy: A systematic review. International Journal of Educational Development, 94.
- Brody, N. (1997). Intelligence, schooling, and society. American Psychologist, 52(10), 1046–1050.
- BRUNI, O., FERINISTRAMBI, L., RUSSO, P., ANTIGNANI, M., INNOCENZI, M., OTTAVIANO, P., VALENTE, D., & OTTAVIANO, S. (2006). Sleep disturbances and teacher ratings of school achievement and temperament in children. Sleep Medicine, 7(1), 43–48.
- Cefai, C., et al. (2022). “The Effectiveness of a School-Based, Universal Mental Health Programme in Six European Countries.†Frontiers in Psychology 13.
- Chambers *, E. A., & Schreiber, J. B. (2004). Girls' academic achievement: varying associations of extracurricular activities. Gender and Education, 16(3), 327–346.
- Chamorro-Premuzic, T., Quiroga, M. A., & Colom, R. (2009). Intellectual competence and academic performance: A Spanish study. Learning and Individual Differences, 19(4), 486–491.
- Chandrasekhar, S., & Mukhopadhyay, A. (2006). Primary Education as a Fundamental Right: Cost Implications. SSRN Electronic Journal. 3797–3804.
- Cheers, B. (1990). Rural Disadvantage in Australia. Australian Social Work, 43(1), 5–13.
- Chege, F. N. (2007). Education and Empowerment of Girls against Gender- based Violence. Journal of International Cooperation in Education, 10(1), 53–70.
- Colom, R., & Flores-Mendoza, C. (2007). Intelligence predicts scholastic achievement irrespective of SES factors: Evidence from Brazil. Intelligence, 35(3), 243–251.
- Crosnoe, R., Johnson, M., & Elder, G. H. (2004). School Size and the Interpersonal Side of Education: An Examination of Race/Ethnicity and Organizational Context*. Social Science Quarterly, 85(5), 1259–1274.
- Deary, I. J., Strand, S., Smith, P., & Fernandes, C. (2007). Intelligence and educational achievement. Intelligence, 35(1), 13–21.
- Eitle, T. M. (2005). DO GENDER AND RACE MATTER? EXPLAINING THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SPORTS PARTICIPATION AND ACHIEVEMENT. Sociological Spectrum, 25(2), 177–195.
- Shafiq, M., & Berhanu, G. (2011). FACTORS AFFECTING STUDENT QUALITY OF ACADEMIC PERFORMANCE: A CASE OF SECONDARY SCHOOL LEVEL. Journal of Quality and Technology Management, 7(2), 1–14.
- Fiske, E. B. (2012). World atlas of gender equality in education. Unesco.
- G, Honorati, Maddalena,Gentilini,Ugo,Yemtsov,Ruslan . n.d. “The State of Social Safety Nets 2015.†Text/HTML. World Bank. Accessed September 13, 2022.
- Gorman, K. S., & Pollitt, E. (1996). Does Schooling Buffer the Effects of Early Risk? Child Development, 67(2), 314.
- Goss, H. (2022). Student Learning Outcomes Assessment in Higher Education and in Academic Libraries: A Review of the Literature. The Journal of Academic Librarianship, 48(2), 102485.
- Gottfredson, L. S. (2002). g: Highly General and Highly Practical. In In The General Factor of Intelligence.
- Gustafsson, J., & Undheim, J. O. (1996). Individual differences in cognitive functions. Az.
- Habibullah, S., & Ashraf, J. (2013). Factors Affecting Academic Performance of Primary School Children. Pakistan Journal of Medical Research, 52(2), 47–57.
- Hanushek, Eric A., and Ludger Woessmann. 2017. “School Resources and Student Achievement: A Review of Cross-Country Economic Research.â€
- Jehan, N., & Idris, M. (2019). Costing out Educational Needs for Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. Global Social Sciences Review, IV(II), 34–42.
- Jensen, A. R. (1998). Human Evolution, Behavior, and Intelligence. The g Factor: The Science of Mental Ability. Praeger Publishers/Greenwood Publishing Group Westport, CT, US.
- Kaguamba, M. M. (2011). Factors affecting boys' academic performance in public primary schools in Kieni West District, Kenya. Erepository.uonbi.ac.ke. h
- Klusmann, U., Aldrup, K., Roloff, J., Lüdtke, O., & Hamre, B. K. (2021). Does instructional quality mediate the link between teachers' emotional exhaustion and student outcomes? A large-scale study using teacher and student reports. Journal of Educational Psychology, 114(6), 1442–1460.
- Kuncel, N. R., Hezlett, S. A., & Ones, D. S. (2004). Academic Performance, Career Potential, Creativity, and Job Performance: Can One Construct Predict Them All? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 86(1), 148–161.
- Kyttälä, M., & Lehto, J. E. (2008). Some factors underlying mathematical performance: The role of visuospatial working memory and non-verbal intelligence. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 23(1), 77–94.
- Laidra, K., Pullmann, H., & Allik, J. (2007). Personality and intelligence as predictors of academic achievement: A cross- sectional study from elementary to secondary school. Personality and Individual Differences, 42(3), 441–451.
- Legewie, J., & DiPrete, T. A. (2012). School Context and the Gender Gap in Educational Achievement. American Sociological Review, 77(3), 463–485.
- Lemos, G. C., Abad, F. J., Almeida, L. S., & Colom, R. (2014). Past and future academic experiences are related to present scholastic achievement when intelligence is controlled. Learning and Individual Differences, 32, 148–155.
- Liouaeddine, M., Bijou, M., & Naji, F. (2018). The Main Determinants of Moroccan Student Outcomes. American Journal of Educational Research, 5(4), 367–383.
- Liu, J., Peng, P., & Luo, L. (2019). The Relation between Family Socioeconomic Status and Academic Achievement in China: A Meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 32(1), 49–76.
- Maldonado, J. E., & De Witte, K. (2021). The effect of school closures on standardised student test outcomes. British Educational Research Journal, 48(1).
- McCoy, L. P. (2005). Effect of Demographic and Personal Variables on Achievement in Eighth-Grade Algebra. The Journal of Educational Research, 98(3), 131–135.
- Millette, A. (1988). Tes / Kelle Lectures on Educational Leadership in the Millennium “Professionals, Pedagogy and Leadershipâ€. A lecture given on 3 June 1988.
- Neisser, U., Boodoo, G., Bouchard, T. J., Jr., Boykin, A. W., Brody, N., Ceci, S. J., Halpern, D. F., Loehlin, J. C., Perloff, R., Sternberg, R. J., & Urbina, S. (1996). Intelligence: Knowns and unknowns. American Psychologist, 51(2), 77–101.
- OECD. (2005). School Factors Related to Quality and Equity: Results from PISA 2000. In OECD iLibrary. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
- Panskyi, T., Korzeniewska, E., Serwach, M., & Grudzie, K. (2021). New realities for Polish primary school informatics education affected by COVID- 19. Education and Information Technologies, 27(4), 5005–5032.
- Peng, S. S. (1995). Understanding Racial- Ethnic Differences in Secondary School Science and Mathematics Achievement. Research and Development Report. ERIC.
- Primi, R., Ferrão, M. E., & Almeida, L. S. (2010). Fluid intelligence as a predictor of learning: A longitudinal multilevel approach applied to math. Learning and Individual Differences, 20(5), 446–451
- Rahman, A. U., & Uddin, S. (2009). Statistical Analysis of Different Socio-Economic Factors Affecting Education of N-W.F.P (Pakistan). Journal of Applied Quantitative Methods, 4(1), 88–94
- Reed, R. L. (1976). A comparative study of primary school social studies in three Australian states: Victoria, New South Wales and Western Australia: 1952-1975. Unpublished M.Ed thesis, University of Melbourne.
- Reid, Ken. 1983. “Retrospection and Persistent School Absenteeism.†Educational Research 25 (2): 110–15.
- Renn, K. (1983). Retrospection and persistent school absenteeism. Educational Research, 25(2), 110–115.
- Rosander, P., Bäckström, M., & Stenberg, G. (2011). Personality traits and general intelligence as predictors of academic performance: A structural equation modelling approach. Learning and Individual Differences, 21(5), 590–596.
- Ruiz, L. D., McMahon, S. D., & Jason, L. A. (2018). The Role of Neighborhood Context and School Climate in School- Level Academic Achievement. American Journal of Community Psychology, 61(3- 4), 296–309.
- Ryan, G., Callaghan, S., Rafferty, A., Higgins, M., Mangina, E., & McAuliffe, F. (2021). Learning outcomes of immersive technologies in healthcare student education: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 24(2), e30082.
- Saha, L. J. (1983). Social Structure and Teacher Effects on Academic Achievement: A Comparative Analysis. Comparative Education Review, 27(1), 69–88.
- Sattler, J. M., & Ryan, J. J. (2009). Assessment with the WAIS-IV. Jerome M. Sattler Publisher, Inc.
- Shah, D., Haider, G., & Taj, T. (2019). Causes of Dropout Rate at Primary Level in Pakistan. International Journal of Curriculum and Instruction, 11(2), 38– 74.
- Siddiqui, N., & Gorard, S. (2017). Comparing government and private schools in Pakistan: The way forward for universal education. International Journal of Educational Research, 82, 159–169.
- Simon, H. (1980). Problem solving and education. Problem Solving and Education: Issues in Teaching and Research, 81–96.
- Taub, G. E., Keith, T. Z., Floyd, R. G., & Mcgrew, K. S. (2008). Effects of general and broad cognitive abilities on mathematics achievement. School Psychology Quarterly, 23(2), 187–198.
- Taylor, C. (2018). The Reliability of Free School Meal Eligibility as a Measure of Socio-Economic Disadvantage: Evidence from the Millennium Cohort Study in Wales. British Journal of Educational Studies, 66(1), 29–51.
- Thomson, S. (2018). Achievement at school and socioeconomic background—an educational perspective. Npj Science of Learning, 3(1), 1–2.
- Ubogu, R. E. (2004). The Causes of Absenteeism and Dropout among Secondary School Students in Delta Central Senatorial District of Delta State. Unpublished PhD Thesis, Delta State University, Nigeria: Abraka.
- Unterhalter, U. (2003). Education, Capabilities and Social Justice. Chapter Prepared for UNESCO
- EFA Monitoring Report 4.
- Vavrus, F., & Moshi, G. C. (2009). The Cost of a “Free†Primary Education in Tanzania. 2(1), 31–42.
- Villena- Taranilla, R., Tirado-Olivares, S., Cózar-Gutiérrez, R., & González-Calero, J. A. (2022). Effects of virtual reality on learning outcomes in K-6 education: A meta-analysis. Educational Research Review, 35, 100434.
- Vourletsis, I., Politis, P. (2022). Developing Computational Thinking Practices in Primary Education. Outcomes from a School-Year Instructional Intervention. In: Reis, A., Barroso, J., Martins, P., Jimoyiannis, A., Huang, R.YM., Henriques, R. (eds) Technology and Innovation in Learning, Teaching and Education. TECH-EDU 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1720. Springer, Cham.
- Vourletsis, I., Politis, P. (2022). Developing Computational Thinking Practices in Primary Education. Outcomes from a School-Year Instructional Intervention. In: Reis, A., Barroso, J., Martins, P., Jimoyiannis, A., Huang, R.YM., Henriques, R. (eds) Technology and Innovation in Learning, Teaching and Education. TECH-EDU 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1720. Springer, Cham. h
- Yunita, & Komsi, D. N. (2023). “The Effect of Reading Interest on Learning Outcomes of Primary School Students: Is There Any Difference?†Pedagogy: Indonesian Journal of Teaching Dan Learning Research, 1(1), 21–29.
- World Bank, (2005) (2005). “Internal Efficiency of and Costs of Higher Education in Kenyaâ€. Washington, D.C.: the World Bank.
Cite this article
-
APA : Jehan, N., & Nawaz, F. (2023). Determinants of Percentage Achievements of Public Primary School Students in Northern Pakistan. Global Educational Studies Review, VIII(I), 350-366. https://doi.org/10.31703/gesr.2023(VIII-I).31
-
CHICAGO : Jehan, Noor, and Fahim Nawaz. 2023. "Determinants of Percentage Achievements of Public Primary School Students in Northern Pakistan." Global Educational Studies Review, VIII (I): 350-366 doi: 10.31703/gesr.2023(VIII-I).31
-
HARVARD : JEHAN, N. & NAWAZ, F. 2023. Determinants of Percentage Achievements of Public Primary School Students in Northern Pakistan. Global Educational Studies Review, VIII, 350-366.
-
MHRA : Jehan, Noor, and Fahim Nawaz. 2023. "Determinants of Percentage Achievements of Public Primary School Students in Northern Pakistan." Global Educational Studies Review, VIII: 350-366
-
MLA : Jehan, Noor, and Fahim Nawaz. "Determinants of Percentage Achievements of Public Primary School Students in Northern Pakistan." Global Educational Studies Review, VIII.I (2023): 350-366 Print.
-
OXFORD : Jehan, Noor and Nawaz, Fahim (2023), "Determinants of Percentage Achievements of Public Primary School Students in Northern Pakistan", Global Educational Studies Review, VIII (I), 350-366
-
TURABIAN : Jehan, Noor, and Fahim Nawaz. "Determinants of Percentage Achievements of Public Primary School Students in Northern Pakistan." Global Educational Studies Review VIII, no. I (2023): 350-366. https://doi.org/10.31703/gesr.2023(VIII-I).31
