Abstract
This study explores the impact of PEELI training on head teachers in Multan, Punjab, Pakistan, focusing on their pivotal role in school performance. A sample of 416 participants, equally divided between trained and untrained head teachers, was selected through random sampling. Data was collected using questionnaires and checklists and analyzed using SPSS-11 software. This descriptive study found that PEELI training significantly enhances head teachers' awareness of children's right to education, barriers to accessing education, and effective resource utilization. Trained head teachers demonstrated better practices in using learning aids and maintaining hygienic school conditions, highlighting the importance of in-service training for educational leaders.
Key Words
PEELI (Punjab Education and English Language Initiative), Leadership, Education, Management System
Introduction
Literature Review
Traits are said to be specific qualities or characteristics of a person that one should possess to complete his/her professional duties. Every profession needs some specialized traits or qualities to work efficiently. These traits are professional values to use productively and efficiently in the workplace that vary concerning profession and duties. It is a role to aspire to and work towards the bigger responsibilities. Without proper administration and coordination of all the participants in the education to achieve the targets and goals is not possible. According to Dubrin and Dalglish (2002) and Hargreaves (2003), school improvement requires effective leadership and management at the school level that a skilled person can do. These skills are produced among head teachers through training and the success of training can only be measured on the base of what people have learned that is by their practices in their workplace (Fullan, 2015; Okumbe, 2007). So, training conducted in aspects of training observed in PEELI training are discussed here and are categorized into two; to have knowledge and to practice in the workplace.
Knowledge of Head Teachers
Among the traits needed for head teachers, some of these should be aware of them that are as follows:
Child rights to education and barriers: According to the constitution of Pakistan 1973, Article 37-B and 38-D education is a fundamental and basic right of every citizen. A head teacher of a primary school should be aware of this and remove the hurdles in getting admission to school. These barriers vary with respect to region. Some of these are;
Societal factors: According to Demir and Sangiovanni-Vincentelli's (1998) study, poverty, lack of awareness about the importance of education, family culture, and number of family members at home. A lot of steps have been taken to eradicate illiteracy and overcome these hurdles with the help of different donor agencies. According to reports by the World Bank (2005) and UNESCO (2007), there is progress in achieving universal primary education goals due to steps taken, such as stipends for girls, free books, Early Child Education (ECE) rooms, etc. The literature on investment in free primary education improves access to school, particularly for children from poor, rural families and for girls and the disabled (Colclough & Lewin, 1993; & Birdsall, Levine, & Ibrahim, 2005; Lewin, 2007; Greeley, 2007; & Fredriksen, 2009). Especially the availability of schools in rural areas, infrastructure, including buildings, playground sitting desks, etc. serves to increase enrollment (Lehman, 2003; & Burde & Linden, 2009).
Barriers of Poverty: Poverty is considered a major barrier to education especially when there is unemployment pervaded. It is assumed that education means investment for prestigious income in the form of a job. Obviously, income affects education when direct costs of school are involved, such as school fees, books, uniforms, transport, etc. (Lewis & Lockheed, 2006; King & Walle, 2007; Fredriksen, 2009). In Pakistan, poor children usually live closer to schools with fewer resources, and often education of a low quality also affects enrolment (World Bank, 2004; Lewis & Lockheed, 2006). Families make choices about whether they will send their children to school or use their children's time for household chores or outside labor more for girls living in rural areas. (Hunte, 2005; Lewis & Lockheed, 2006; Lewin, 2007)
According to a report by UNESCO (2008) globally, four out of five children who are out of school live in rural areas and the majority (53%-56%) of these are girls. Yet this problem has been solved in the province of Punjab to some extent. In spite of that, a head teacher should be aware of that and solve the problem of needy children by collecting donations or funds.
So, it is the head teachers' responsibility to visit the parents of out-of-school children and convince them to send their children to school by telling them the importance of education.
Practices of Head Teachers in School
Headteachers play multi-dimensional roles in his/her workplace. According to Zuccolo, Diaz, Jemeneze, and Braakman (2003) in primary school, the main outcome is students' learning achievement and head teachers have a strong influence on students. Trained and experienced headteachers tend to perform better in the provision of learning material. According to the guide for "Roles and responsibilities of head teachers" published by Sydney Distance Education High School in 2022, the major roles of heads are leading and practicing.
Effective utilization of resources; financial, teaching, and learning material: It is a managerial skill to utilize available resources for the best use especially that helps in learning at school. Researchers (Bird, 2006; Hollander, 1978; Ibukun & Oyewole, 1997; Peterson, 2004; Triandis, 2006) identified personal qualities of successful leaders such as; courage, wisdom, and counselor while character an example of those traits, said to make an individual leader to ensure effectiveness for a particular set of leader functions. Hence, the ability of leaders is relative to the specific social unit or organization (Yukl, 2002; Thomas &Inkson, 2004; Earley& Mosakowski, 2004). The quality of leadership makes a significant difference to school and student outcomes.
According to the PEELI module of training for head teachers, the aspects that one should practice in his/her workplace are; counseling the teachers and SMC, parents, and community members, providing learning material in the class, checking the teachers' activities in the class, provide students' need and utilize funds to run the school in a better way. Resources that are in the form of funds available as NSB (non-salary budget) can be utilized for hygienic conditions (water, cleaning the school, provision of washrooms, etc.), and instructional resources. The head teacher's responsibility is to involve the community to fulfill the requirements.
Research Methodology
This is a descriptive study in nature in which a mixed-method was used to study the impact of training on Primary schools’ Head Teachers on their Management Skills. Due to having a large population, the survey method was used to have maximum responses. To collect the required information, a questionnaire was used with a checklist for observation.
Population and Sample
The population of this study was head teachers of district Multan. A multistage random sampling technique was used in this study. Two tehsils were considered in this research work schools were selected with equal numbers of males and females as well as rural and urban. The sample comprised four hundred and sixteen (416) head teachers and schools. The sample size was selected with the number of schools with the help of a chart by Cohen, Manion & Morrison, 2007, p-106) at a 95% confidence level.
Table 1
|
Tehsil |
Gender |
Total schools |
Sample schools |
Trained Heads |
Not-trained Heads |
Total sample |
|
Multan Sadder |
Male |
153 |
110 |
65 |
65 |
264 |
|
Female |
258 |
154 |
67 |
67 |
||
|
Jalalpur peer wala |
Male |
78 |
66 |
33 |
33 |
152 |
|
Female |
111 |
86 |
43 |
43 |
||
|
Total |
600 |
416 |
208 |
208 |
416 |
|
Research instruments
Two tools were used; a questionnaire and a checklist. In the questionnaire, questions were asked by head teachers about training, benefits of training, and skills developed in training. The checklist was used for physical verification of teaching facilities provided by the head teachers in their schools. It has two major parts, one is about producing awareness among head teachers' responsibilities and the second is about practices; provision of resources, and observing teachers.
? Awareness: child's right to education, the financial condition of people, attitude of people towards education, issues of students towards education, barrios (financial, culture, family size)
? Practices: Counsel SMC, donors, parents, and teachers, check teachers in the class and their diaries, provide resources in the class as; modules, teaching kit, charts, maps, and tabs for LND practice and also observe whether a teacher is using available resources for teaching, provide water for drinking and cleaning
Checklist: cleanliness of classrooms, grounds, toilets, water, students in uniform, cleanliness of students as nails, uniform, hair, bags
Data collection
Data was collected by personal visits of the schools. Prior to handing over the questionnaire the objective of it was explained to the respondents. The checklist was filled out by visiting the school.
Data analysis and results
The data was analyzed with the help of SPSS_21 software by giving values;
Not at all: 1, Slightly aware: 2, Somewhat aware: 3, Moderately aware: 4, Extremely: 5 and in checklist; Never: 1, Ever: 2, Sometime: 3, Frequently: 4, Always: 5
Table 2
|
Number of trainings |
Child right |
Financial Barrier |
Family |
Counselling SMC |
Multi-grade class |
Teachers in class |
Provide physical resources |
Kit in class |
|
Not-trained |
2.99 |
3.60 |
3.75 |
3.74 |
3.13 |
3.54 |
3.61 |
2.98 |
|
Trained |
3.32 |
3.70 |
3.76 |
3.65 |
3.51 |
3.49 |
3.60 |
2.96 |
Table 3
|
|
Cleanliness |
Cleanliness of students |
Water |
First-aid box |
||||
|
|
Rooms |
Toilets |
Grounds |
Nails |
Hair-cut |
Uniform |
||
|
Not-trained |
78.80% |
87.55% |
94.20% |
96.20% |
92.80% |
98.88% |
100% |
85.55% |
|
Trained |
88.45% |
86.89% |
100% |
98.80% |
96.50% |
99.00% |
100% |
96.78% |
Figure 1
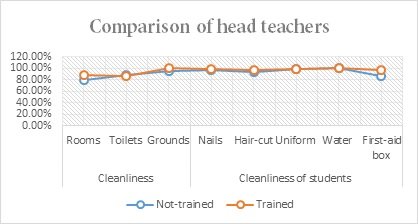
The given graph is about the comparative results of head teachers. It indicates that the head teachers trained by PEELI observe more hygienic conditions of classrooms and grounds as compared to the heads not trained. In the same way, PEELI training has more impact on observing students' cleanliness, especially about students' nails and haircuts while head teachers not trained are less aware and practice in this case. In the case of the importance and availability of first-aid boxes in the school trained head teachers practice better as compared to not-trained head teachers.
Conclusion and Discussion
This study was designed to see the impact of PEELI training on head teachers that is provided during service. Training develops skills and enhances the knowledge of practices that are needed in the workplace (Memon, 2007). In this respect, the Punjab Education and English Initiative (PEELI) started to train head teachers along with the teachers to develop knowledge and skills to meet the needs of the changing scenario. It was assumed that it would help to enable head teachers and education managers to understand the importance and benefits of changes and support the teachers in their schools in its implementation. According to the training module for head teachers, there were two major objectives; to have knowledge and awareness of child rights to education, barriers to enrollment and retention, the importance of healthy food, hygiene and practice, effective classroom management in multigrade classroom situations, provision of resources to create hygienic condition (water, cleanliness), teaching material, increase community involvement in the school improvement (NSB and SMC members), enhance head teachers’ knowledge and skills for school management and us of fund where needed. This study was conducted in the district of Multan, Punjab, Pakistan. Views of the head teachers were collected with the help of a self-respondent questionnaire and a checklist to see resources.
The results indicate that teachers got clear benefits of training in having got the importance of education and right of every child of school going age to education, have right to be admitted in school, knowledge of financial barriers of children to get admission in school and using teaching material and teaching-aids needed for multigrade with respect to provision resources in the school.
It was also observed that the head teachers trained by PEELI observed more, cleanliness conditions of the classroom and grounds as compared to the heads not-trained. In the same way, PEELI training has more impact on observing students' cleanliness especially about students' nails and haircuts while head teachers not-trained are less aware and practice less in this case. In the case of the importance and availability of first-aid boxes in the school trained head teachers are more aware of its importance and ensure its availability in the school as compared to not-trained head teachers.
The overall result indicates that the trained head teachers are performing better as compared to those who have not got training in the school in the aspects in which they have got training. Thus it is suggested to conduct training for teachers and head teachers in other aspects (subject knowledge, pedagogy) as well. It is also suggested to conduct their training after a specific tenure that may be three years or so.
References
-
Okumbe, J. A. (2007). Educational management: Theory and practice. Nairobi University Press.
Google Scholar Fulltext - Fullan, M. (2015). The New Meaning of Educational Change, Fifth Edition. Teachers College Press. Google Scholar Fulltext
- Bird, R. B., Stewart, W. E., & Lightfoot, E. N. (2006). Transport phenomena. John Wiley & Sons. Google Scholar Fulltext
- Birdsall, N., Levine, R., & Ibrahim, A. (2005). Towards Universal Primary Education: investments, incentives, and institutions. European Journal of Education, 40(3), 337–349. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1465-3435.2005.00230.x Google Scholar Fulltext
- Colclough, C., & Lewin, K. M. (1993). Educating all the children: Strategies for primary schooling in the South. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BA20293721 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Demir, A., & Sangiovanni-Vincentelli, A. (1998). Analysis and simulation of noise in nonlinear electronic circuits and systems. Springer. Google Scholar Fulltext
- DuBrin, A. J., & Dalglish, C. (2002). Leadership, an Australasian focus. Google Scholar Fulltext
- Hargreaves, A., & Fink, D. (2003). Sustaining leadership. Phi Delta Kappan/˜the œPhi Delta Kappan, 84(9), 693–700. https://doi.org/10.1177/003172170308400910 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Hunte, P. (2005). Household decision-making and school enrolment in Afghanistan: Case study 3: Nesher villages, Belcheragh district, Faryab province. Afghanistan Research and Evaluation Unit. Google Scholar Fulltext
- Ibukun, W. O. (1997). Educational management: Theory and practice (pp. 42-57). Greenland Publishers. Google Scholar Fulltext
- King, E. M., & van de Walle, D. (2007). Girls in Lao PDR: Ethnic affiliation, poverty, and location. In M. Lewis & M. Lockheed (Eds.), Exclusion, gender and education: Case studies from the developing world. Washington, DC: Center for Global Development. Google Scholar Fulltext
- Lehman, D. (2003). Bringing the school to the children : Shortening the path to EFA. World Bank Other Operational Studies, 1–3. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/10986/10377/1/268840PAPER0Ed1al0Access0Initiative.pdf Google Scholar Fulltext
- Lewin, K. M. (2007). Improving access, equity and transitions in education: Creating a research agenda (Research Monograph No. 1). Brighton, UK: Consortium for Research on Educational Access, Transitions and Equity (CREATE). Google Scholar Fulltext
- Lewis, M. A., & Lockheed, M. E. (2006). Inexcusable Absence: Why 60 Million Girls Still Aren't in School and What To Do About It. https://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BA81314596 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Peterson, C., Seligman, M. E. P., & Seligman, F. L. P. O. P. M. E. P., PhD. (2004). Character strengths and virtues: A Handbook and Classification. Oxford University Press. Google Scholar Fulltext
- Triandis, H. C. (2006). Cultural intelligence in organizations. Group & Organization Management, 31(1), 20–26. https://doi.org/10.1177/1059601105275253 Google Scholar Fulltext
- Vivas, A., Gelaye, B., Aboset, N., Kumie, A., Berhane, Y., & Williams, M. A. (2010). Knowledge, attitudes and practices (KAP) of hygiene among school children in Angolela, Ethiopia. PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21155409 Google Scholar Fulltext
- World Bank. (2005). Le système éducatif de la république démocratique du Congo : Priorités et alternatives (No. 68). Washington, DC: World Bank, Africa Region. Google Scholar Fulltext
- Yukl, G. A. (2002). Leadership in organizations. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Cite this article
-
APA : Arshad, M., Hussain, M., & Iqbal, Z. (2024). Leadership Styles and School Performance: A Comparative Analysis of PEELI-Trained and Non-PEELI-Trained Head Teachers. Global Educational Studies Review, IX(II), 51-58. https://doi.org/10.31703/gesr.2024(IX-II).07
-
CHICAGO : Arshad, Muhammad, Munawar Hussain, and Zafar Iqbal. 2024. "Leadership Styles and School Performance: A Comparative Analysis of PEELI-Trained and Non-PEELI-Trained Head Teachers." Global Educational Studies Review, IX (II): 51-58 doi: 10.31703/gesr.2024(IX-II).07
-
HARVARD : ARSHAD, M., HUSSAIN, M. & IQBAL, Z. 2024. Leadership Styles and School Performance: A Comparative Analysis of PEELI-Trained and Non-PEELI-Trained Head Teachers. Global Educational Studies Review, IX, 51-58.
-
MHRA : Arshad, Muhammad, Munawar Hussain, and Zafar Iqbal. 2024. "Leadership Styles and School Performance: A Comparative Analysis of PEELI-Trained and Non-PEELI-Trained Head Teachers." Global Educational Studies Review, IX: 51-58
-
MLA : Arshad, Muhammad, Munawar Hussain, and Zafar Iqbal. "Leadership Styles and School Performance: A Comparative Analysis of PEELI-Trained and Non-PEELI-Trained Head Teachers." Global Educational Studies Review, IX.II (2024): 51-58 Print.
-
OXFORD : Arshad, Muhammad, Hussain, Munawar, and Iqbal, Zafar (2024), "Leadership Styles and School Performance: A Comparative Analysis of PEELI-Trained and Non-PEELI-Trained Head Teachers", Global Educational Studies Review, IX (II), 51-58
-
TURABIAN : Arshad, Muhammad, Munawar Hussain, and Zafar Iqbal. "Leadership Styles and School Performance: A Comparative Analysis of PEELI-Trained and Non-PEELI-Trained Head Teachers." Global Educational Studies Review IX, no. II (2024): 51-58. https://doi.org/10.31703/gesr.2024(IX-II).07
